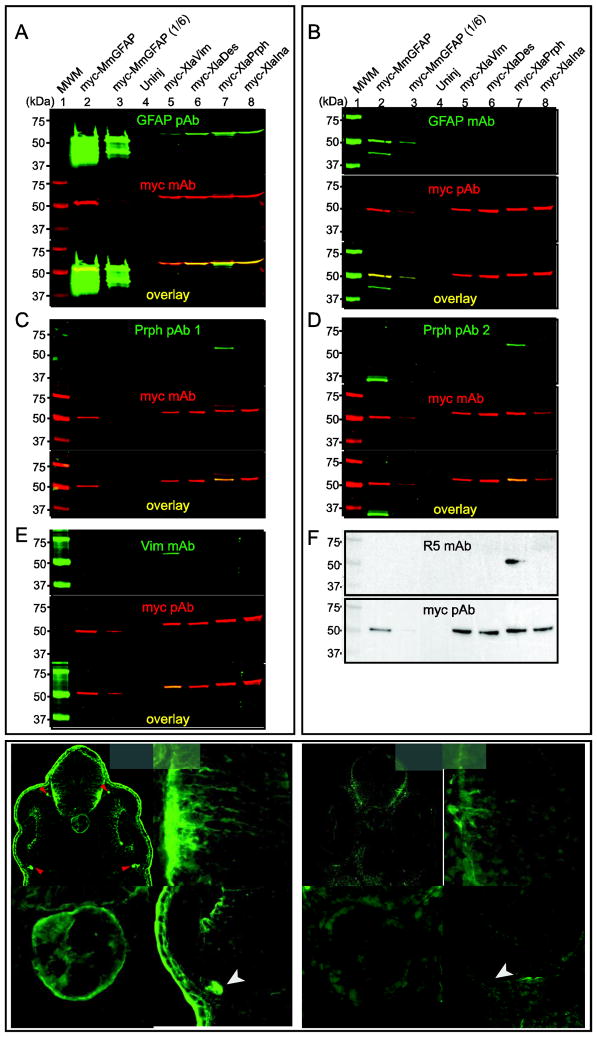
Figure 4. Specificity of intermediate filament protein antibodies.
Western blots were used to determine the specificity of GFAP pAb (A), GFAP mAb (B), Prph pAb 1 (C), Prph pAb 2 (D), Vim mAb (E), and R5 mAb (F). Extracts were prepared from embryos injected with mRNA coding for the indicated myc-tagged IFP. Blots were probed with the indicated combination of primary antibodies. Green fluorescent secondary antibodies were used to detect the IFP and myc primary antibodies, respectively (A–E). Red fluorescent signals were pseudocolored to make visualization easier. Merged images indicate myc-IFP proteins detected by both antibodies (A–E, yellow). Enhanced chemoluminescence was used to test the specificity of the R5 mAb and myc pAb (F). One-sixth the volume of extract from myc-MmGFAP expressing embryos in lane 2 was used in lane 3. Immunohistochemistry was use to compare the staining pattern of the GFAP pAb (G–G‴) and GFAP mAb (H–H‴) in sections of stage 35/36 X. laevis embryos. G′/H′, G″/H″ and G‴/H‴ show magnified views of the brain, notochord and retina, respectively. Arrow and arrow heads, indicate the location of skin epidermis and ocular motorneuron projections dorsal and ventral to the optic cup, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm.