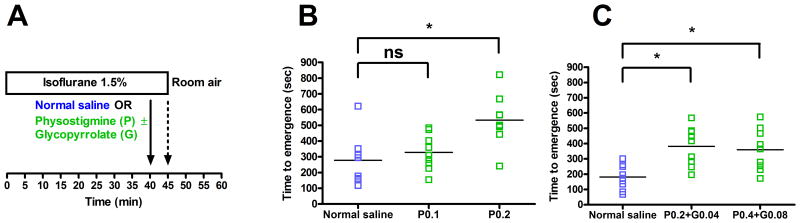
Figure 1. Physostigmine increases time to emergence from isoflurane general anesthesia.
(A) Rats inhaled 1.5% isoflurane in oxygen for 40 min, and then received normal saline or physostigmine ± glycopyrrolate IV (solid arrow). After 5 additional minutes of isoflurane anesthesia, rats were removed from the anesthetizing chamber (dashed arrow) and emergence was defined as return of righting. (B) Scatter plots showing emergence times (n=9). P0.1 = Physostigmine 0.1 mg/kg, P0.2 = physostigmine 0.2 mg/kg. For each data set, the horizontal line represents the mean. (C) Scatter plots showing emergence times for a separate cohort of rats (n=9). P0.2+G0.04 = physostigmine 0.2 mg/kg and glycopyrrolate 0.04 mg/kg, P0.4+G0.08 = physostigmine 0.4 mg/kg and glycopyrrolate 0.08 mg/kg. * Significant difference between groups with 95% confidence.