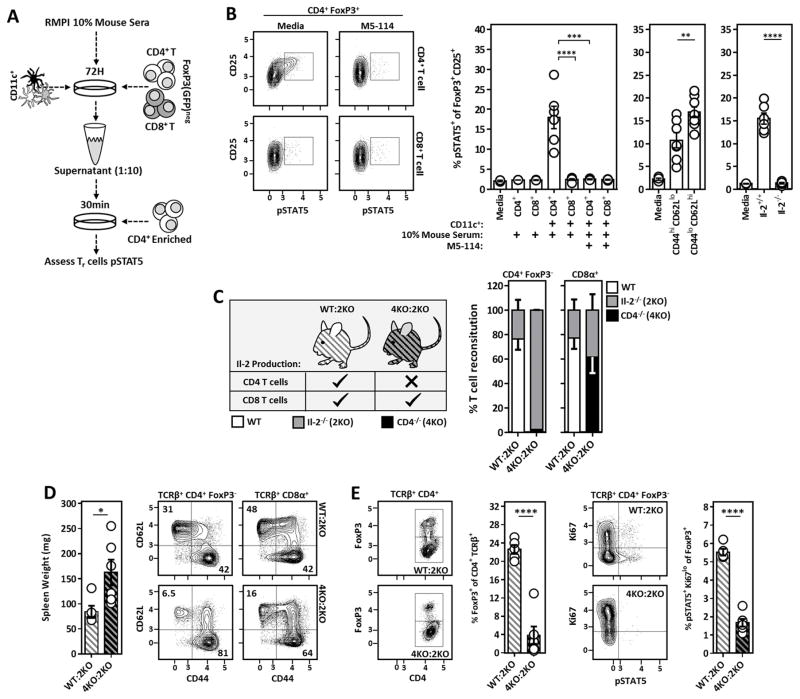
Figure 2. CD4+ T cell-derived Il-2 sustains SLO resident Tr cells and prevents the development of spontaneous autoimmunity.
(A) Experimental design to assess qualitative Il-2 production in DC/T cell co-cultures via bio-assay. (B) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and compiled data (right) assessing pSTAT5 amongst freshly isolated CD4+ FoxP3+ T cells stimulated with 1:10 diluted co-culture supernatants generated as outlined in A. Anti-MHCII (M5-114) antibodies were included in the original co-cultures where indicated. (Middle) Experiments were repeated using sorted CD44hi CD62Llo and CD44lo CD62Lhi CD4+ T cell subsets. (Right) Similar experiments were performed utilizing unfractionated Il-2−/− CD4+ T cells as the co-culture T cell source. The frequency of pSTAT5+ cells amongst CD25+ FoxP3+ T cells is quantified. (C) Design of WT:Il-2−/− and CD4−/−:Il-2−/− chimeras used to assess the requirement of CD4+ vs. CD8+ T cell-derived Il-2 in the maintenance of Il-2 dependent Tr cells in vivo. (Right) Reconstitution analysis of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from WT:Il-2−/− and CD4−/−:Il-2−/− chimeras 5–6 weeks post-reconstitution. ~98% of the CD4+ T cells within CD4−/−:Il-2−/− chimeras were Il-2-deficient. (D) Spleen weight and naïve vs. activated phenotype of splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from WT:Il-2−/− and CD4−/−:Il-2−/− chimeras at time of sacrifice. (E) Analysis of Tr cell frequencies and Il-2 activation (pSTAT5) in splenic Tr cells of the indicated chimeric mice at time of sacrifice. Chimera data is pooled from two independent experiments with at least 2 mice per group. Error bars in all panels represent mean ±SEM. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001, as calculated by unpaired students Student’s t-test (D) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (B).