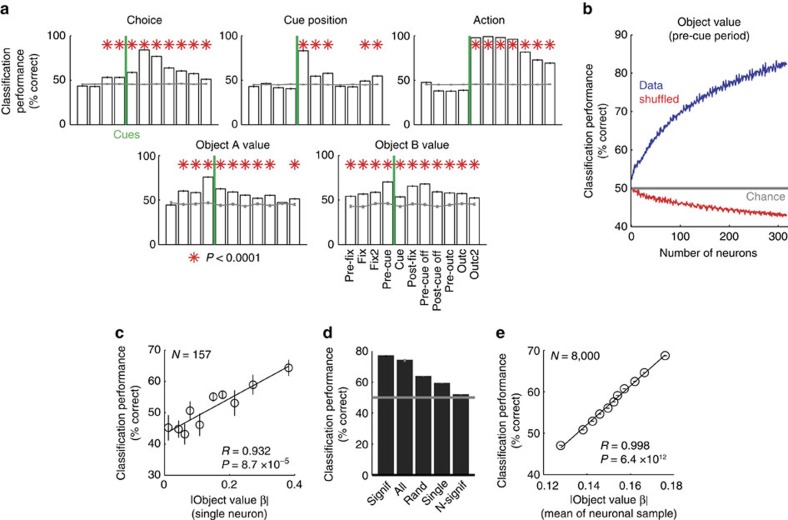
Figure 6. Population decoding of object value.
(a) Performance of a linear support vector machine classifier in decoding object choice, cue position, action and object value across task periods. Performance was measured as cross-validated classification accuracy (% correct, mean±s.e.m.) based on single-trial data from all DLPFC neurons that met inclusion criteria for decoding (N=166 for binary variables choice, cue position and action; N=157 for object value terciles). The grey line in each plot indicates mean (±s.e.m) decoding performance from trial-shuffled data. Red asterisks indicate that decoding accuracy significantly exceeded shuffled decoding (rank-sum test). (b) Object value decoding performance in the pre-cue period increased with the number of neurons. Data for each neuron number show means (±s.e.m) over 10 random combinations of different neurons. The classifier was trained to decode both object A and B value; thus, data from each neuron (N=157) were sampled twice. (c) Object value decoding in individual neurons (in pre-cue period) was related to individual neuron’s value sensitivity (object value linear regression slope). (d) Object value decoding in different sets of neurons (in pre-cue period), depending on individual neuron’s significance of object value regression. Signif: neurons with individually significant object A value regression coefficients (based on randomly chosen subsets of N=20); All: neurons that met inclusion criteria for decoding (N=157); Rand: randomly selected neurons irrespective of object value significance (N=20); Single: single-neuron decoding for all neurons that met inclusion criteria (N=157); N-signif: randomly selected neurons excluding those with significant object value coefficients (N=20). (e) Relationship between decoding performance and single-neuron value sensitivities, tested over randomly selected neuron subsets (8000 samples randomly drawn without replacement, N=20 per sample). Decoding depended on average single-neuron sensitivity (mean unsigned value regression coefficient, averaged over all 20 neurons in each sample).