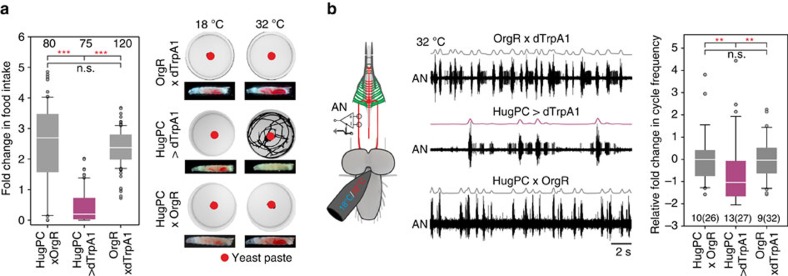
Figure 5. HuginPC neurons modulate feeding and wandering like behaviour.
(a) HugPC-Gal4 line driving UAS-dTrpA1 (n=75 larvae). Larvae show reduction in food intake compared with OrgR × dTrpA1 (n=120 larvae) and HugPC × OrgR (n=80 larvae) (P<0.001, MWU-Test). Controls did not differ from each other (P=0.107, MWU-Test). Activation of huginPC neurons with dTrpA1 induces wandering like behaviour, where larvae leave the appetitive food source yeast. Shown are time projections over 20 min of plates with apple juice agar and a red spot of yeast in the middle. Decrease of food intake was measured as % of red stained gut content compared with the area of the whole larva. (b) Extracellular recordings of the antennal nerve (AN). Activation of huginPC neurons with UAS-dTrpA1 (n=13 larvae, 27 temperature steps) leads to significant decrease in cycle frequency of the AN motor pattern compared with OrgR × dTrpA1 control (n=9 larvae, 32 temperature steps) and HugPC × OrgR control (n=10 larvae, 26 temperature steps) (P=0.003, MWU-Test). Controls did not differ from each other. Significances are indicated as ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 and *P<0.05. Details of descriptive statistics are shown in Supplementary Table 4.