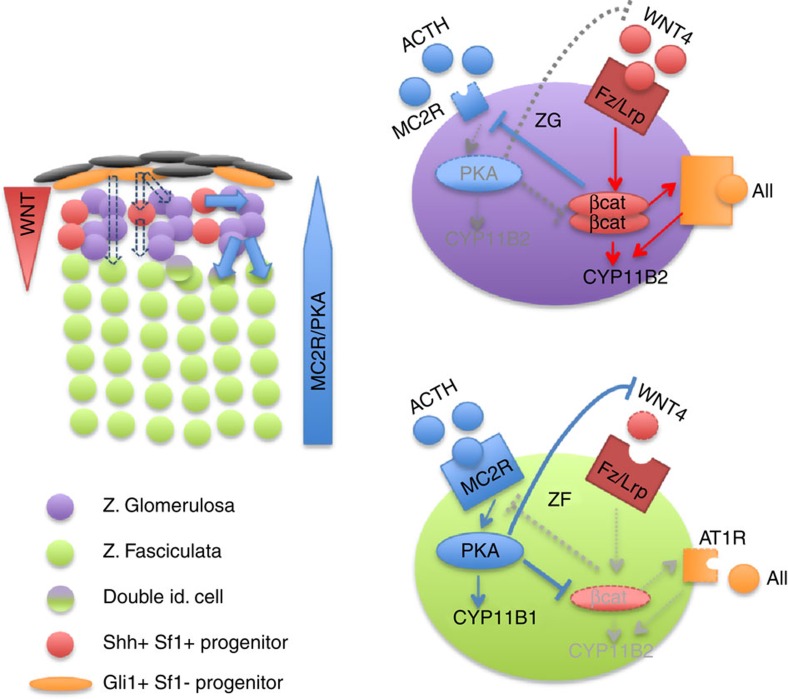
Figure 7. Model for adrenocortical zonal differentiation.
Left panel shows the zonal organization of the adrenal cortex with capsular (orange) and subcapsular (red) progenitor cells, ZG cells (purple), ZF cells (green) and transiting cells with double identity (purple and green). Solid blue arrows show the normal process of cell renewal occurring through recruitment of Shh-positive progenitors that initially differentiate as ZG cells and subsequently differentiate as ZF cells as they migrate within the cortex. Dashed arrows show alternative renewal pathways relying on capsular (Shh-negative) progenitors. Right panels show the interplay between WNT and PKA signalling pathways in ZG cells (purple) and ZF cells (green). Red arrows: activation; blue arrows: inhibition; grey arrows: inactive pathway.