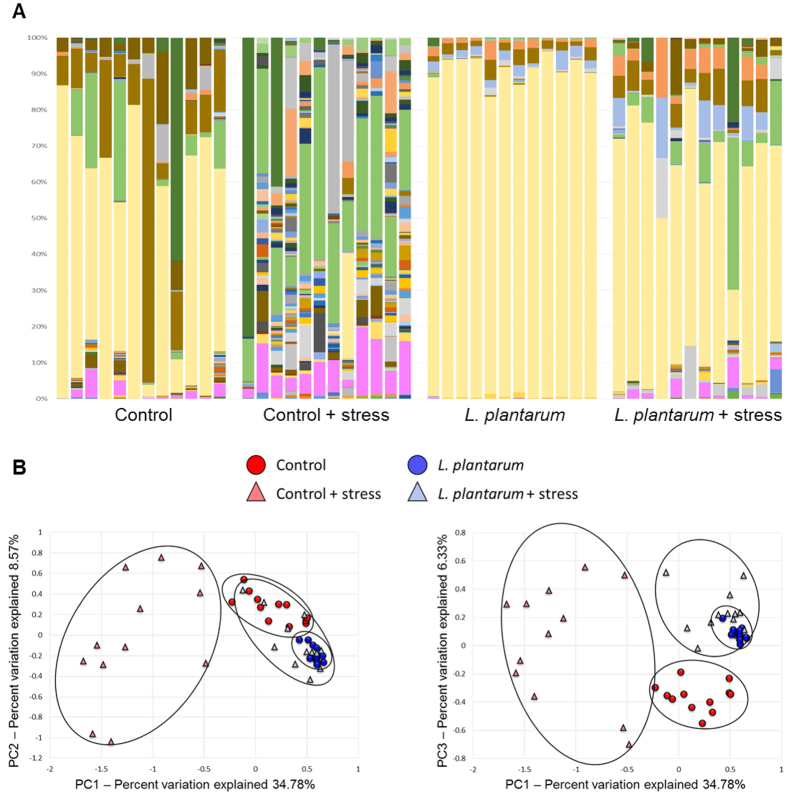
Figure 6. Stress-induced shifts in the GM are attenuated by L. plantarum.
(A‒C) Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) induced dramatic alterations of the GM in control zebrafish, however L. plantarum treatment was shown to be protective against this stress-induced dysbiosis. (A) The relative abundance of the core phylum, Fusobacteria (indicated by the yellow bar), was greatly diminished in the chronically stressed control group, whereas the major core GM remained intact in the chronically stressed L. plantarum treated fish. (B,C) Principal component analysis revealed significant shifts in response to CUS in the control group, while chronically stressed L. plantarum treated zebrafish cluster in conjunction with non-stressed L. plantarum treated fish. (n = 12 fish/group).