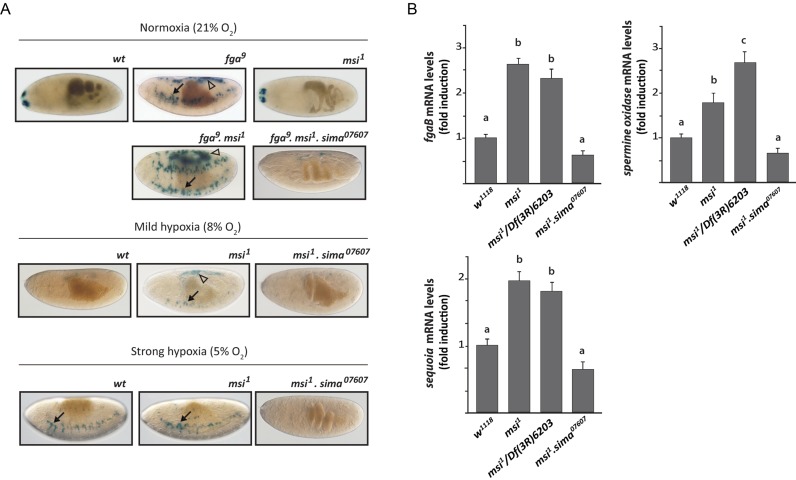
Figure 3.
dMusashi downregulates Sima dependent transcription. (A) Expression of the Sima-inducible reporter HRE-LacZ in wild type, fga9or msi1 mutant embryos maintained in normoxia or exposed to two different hypoxic conditions; arrows indicate groups of tracheal cells that express the reporter with maximal sensitivity, and arrowheads indicate groups of dorsal cells where the reporter expression is more variable but occurs consistently when HIF-dependent transcription is especially strong. In wild type embryos, the reporter is only expressed in strong hypoxia (5% O2 5h), while in fga9 mutants expression can be detected even in normoxia (21% O2), and in msi1 mutants it is already detectable in mild hypoxia (8% O2 5 h); fga9 msi1 double homozygous mutants display overall enhanced expression of the reporter in normoxia in comparison to fga9 single mutants. (B) Expression of three Sima target genes was analyzed by RT-qPCR in wild type, musashi loss-of-function (msi1 homozygous mutants or larvae with the heteroallelic combination msi1/Df(3R)6203) or in msi1 sima07607double homozygous mutant third instar larvae maintained in normoxia. In both msi loss-of-function backgrounds (msi1 or msi1/Df(3R)6203), expression of the three Sima target genes, fgaB, sequoia and spermidine oxidase, is higher than in wild type controls or in msi1 sima07607double mutants. Error bars represent SEM (n = 3; different letters indicate statistical differences with a P < 0.05 in a one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-hoc test).