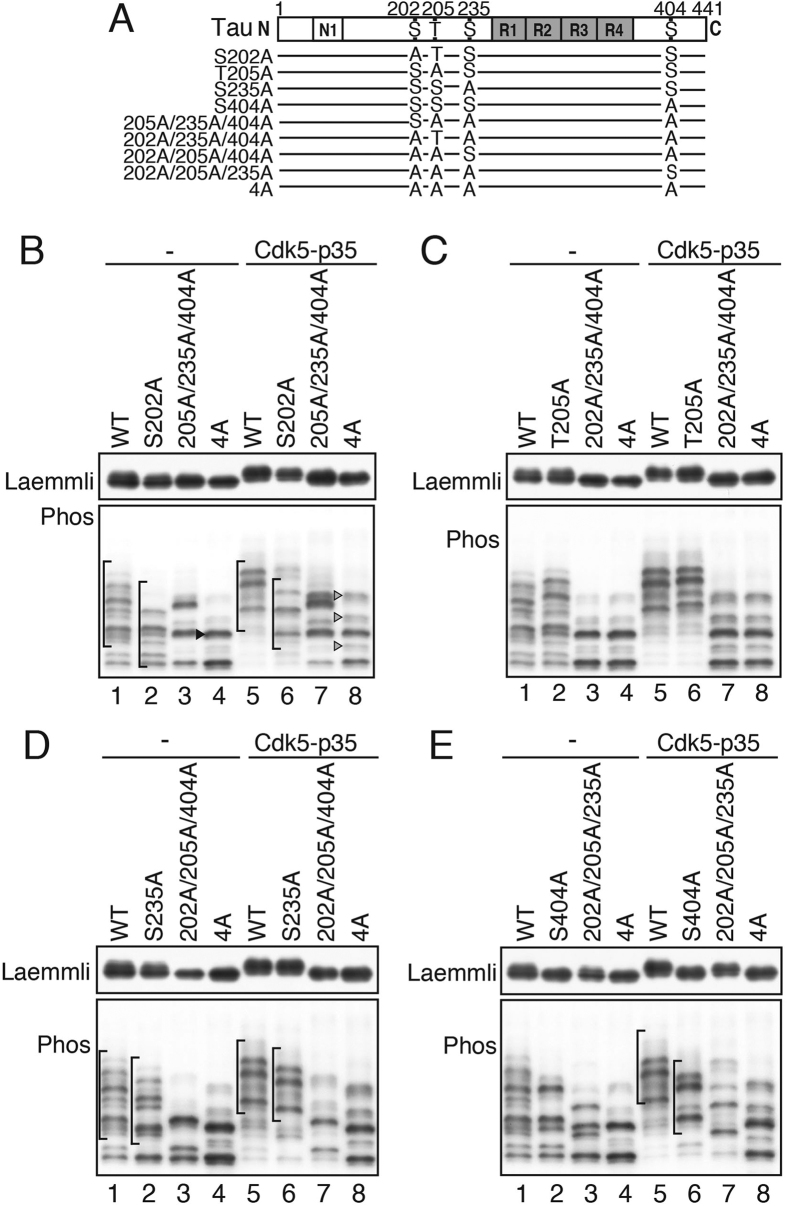
Figure 2. In situ phosphorylation of tau WT and its alanine mutants by Cdk5 in COS-7 cells.
(A) Major Cdk5 phosphorylation sites in tau and their alanine mutants. Amino acids are numbered according to the longest human tau isoform 441. (B)~(E) Tau and its alanine mutants were individually expressed in COS-7 cells in the absence (−) or presence of Cdk5-p35. Their phosphorylation-dependent shifts were examined by immunoblotting with Tau5 after Laemmli’s (upper) or Phos-tag SDS-PAGE (lower). (B) S202A and 205A/235A/404A, (C) T205A and 202A/235A/404A, (D) S235A and 202A/205A/404A, and (E) S404A, and 202A/205A/235A. Arrowhead in lane 4 of (B) indicates a band of tau 4A with a single phosphorylation at a non-Cdk5 site. Arrowheads in lane 8 of (B) indicate bands of tau 4A that were phosphorylated by Cdk5-p35 at sites other than the four major Cdk5-sites. Brackets in (B,D,E) indicate a group of bands that shifted down their mobility as a whole by an Ala mutation of Ser202 (B), Ser235 (D) and Ser404 (E). Immunoblottings of tau after Laemmli’s SDS-PAGE were performed under the same experimental conditions as an example of the uncropped image, which is provided in Supplemental Fig. 3a.