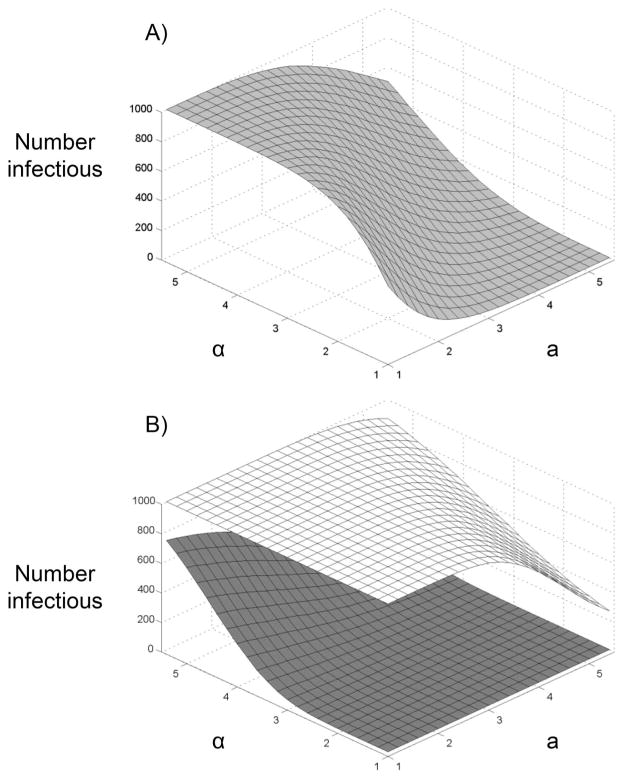
Fig. 2.
Number of infectious mosquitoes is affected by parameters of gamma distribution and offsets. (A) φ = ψ = 500; a is the value of both gamma distribution parameters (a = b) for the number of virions needed for infection; α is the value of both gamma distribution parameters (α = β) for the number of virions in the bloodmeal. The number of infectious mosquitoes is maximized when the number of virions in the bloodmeal has a relatively flat distribution (high α) and the number of virions needed for infection has a relatively peaked distribution (low a). Results were similar when both offsets were 520. (B) Sensitivity to the offset values used. Upper plane (white), ψ = 520 and φ = 500. Bottom plane (gray), ψ = 500 and φ = 520. The infection rate is higher and more sensitive to the shape of the distribution when ψ > φ, as this increases the probability that y > x.