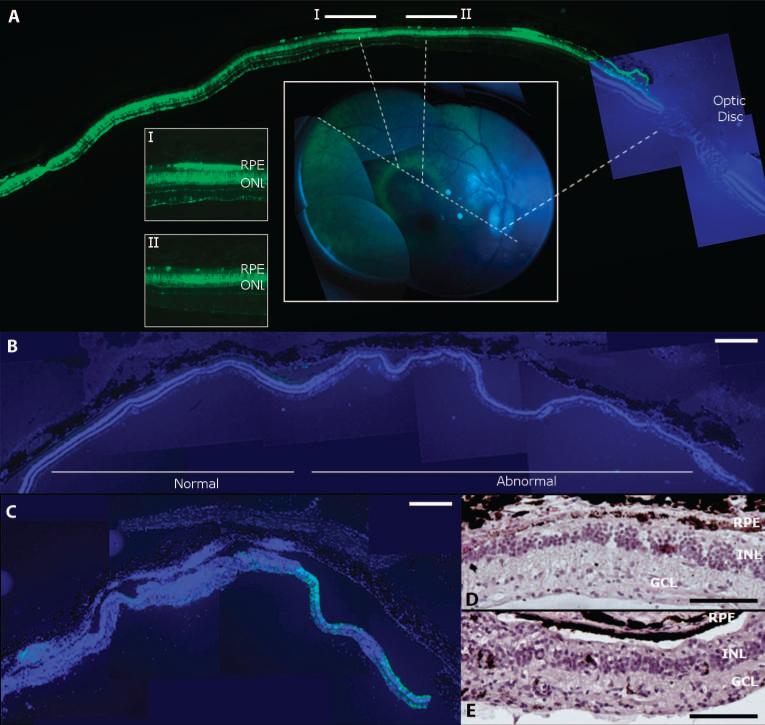
Fig. 2.
Retinal pathology after highest-dose vector injection in monkey retina. (A) Correlating histology and live retinal imaging identifies heterogeneous GFP expression in the vector-exposed part of the retina. A halo-like GFP pattern (green rim) was observed by imaging of the retina (center inset) after a 1011 genome copy dose injection of the AAV2 vector subretinally (animal 18226, right eye). Histology along an axis (center inset, dotted lines) that traverses the bleb, the optic disc, and the halo pattern (I and II) shows that the rims of the GFP halo (see inset I) are defined by GFP-positive RPE (green), whereas adjacent RPE does not express GFP (inset II) (GFP, green; DAPI staining of nuclei, blue). (B) DAPI staining (blue) of a section from a monkey eye injected subretinally with AAV2 (animal 18144, right eye) showing normal outer and inner nuclear layers with only minimal GFP fluorescence (green; left). This section is adjacent to a region where the nuclear layers are disturbed (abnormal; right). (C) Retina from the right eye of monkey 18199 after subretinal injection of AAV8 showing DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) and GFP expression (green) illustrates loss of retinal architecture and GFP on the left while retaining some GFP expression but abnormal retinal structure on the right. (D) Retinal section from animal 18144 (right eye) showing the abnormal portion in (B) stained with H&E. (E) H&E-stained section corresponding to the right part of the retina shown in (C) (animal 18199, right eye). Scale bars, 500 μm [(A) to (C)] and 100 μm [(D) and (E)].