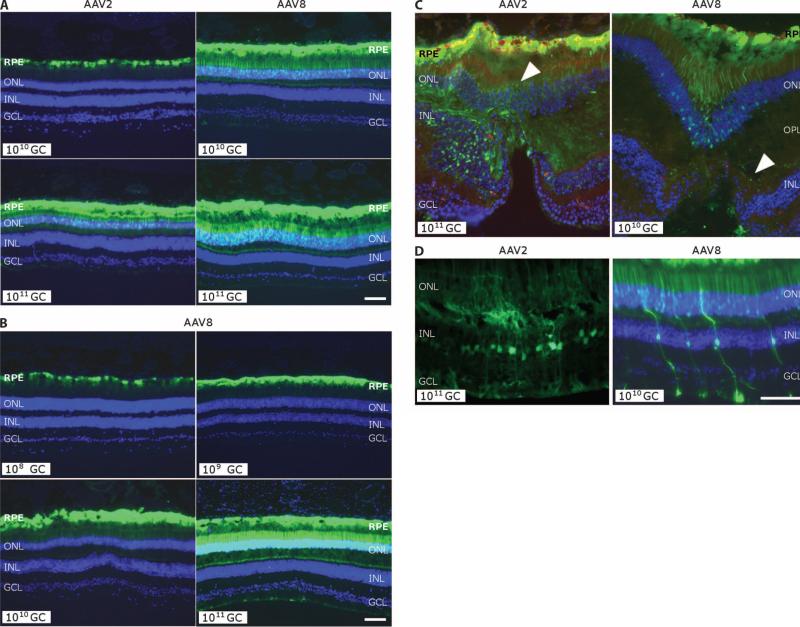
Fig. 3.
GFP transgene expression in the monkey retina. (A) Comparison of GFP expression from histological analysis of monkey retinas after subretinal injection with AAV2 or AAV8 with the designated number of genome copies. Clockwise from top left: animal 18168, left eye; animal 18238, right eye; animal 18155, right eye; animal 18226, right eye. (B) GFP expression after subretinal injection of AAV8 as a function of dose from 108 to 1011 genome copies (GC). Pictures are taken with equal exposure. Due to the intensity of GFP at the high dose, photoreceptor transduction in lower doses is less obvious. Clockwise from top left: animal 18204, left eye; animal 18217, left eye; animal 18208, right eye; animal 18238, right eye. (C) Cellular transduction characteristics after subretinal injection exposing the fovea to 1011 genome copies of AAV2 versus 1010 genome copies of AAV8. Both eyes show strong GFP expression in the RPE, but cone photoreceptors in the foveal pit of the AAV8-injected retina also are GFP-positive, as is the outer plexiform layer (OPL) in the AAV2-exposed retina (indicated by white arrowhead). (D) Transduction of Müller glial cells [with nuclei in the inner nuclear layer (INL)] after injection of AAV2 or AAV8. DAPI stain (blue) shows nuclear layers. Animal 18226, right eye (AAV2); animal 18204, right eye (AAV8). Scale bars, 100 mm. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ONL, outer nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.