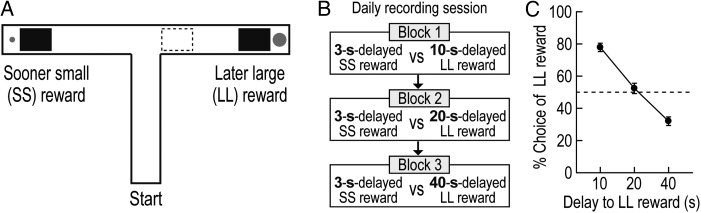
Figure 1.
Choice performance in the delay-based decision-making task. (A) Illustration of the T-maze. Rectangular wooden barriers (black squares) were placed before the food cups on 2 goal arms to control animals' access to SS and LL rewards. When rats chose the goal arm associated with LL reward, an additional barrier (dashed rectangle) was placed at its entrance to prevent the animals from exiting the goal arm during the waiting period. (B) Daily behavioral recording procedures. Three different delays to LL reward were randomly ordered and tested in separate blocks of trials. The delay to SS reward remained unchanged. Each block consisted of forced-choice trials, followed by free-choice trials. (C) Choice preference for LL reward as a function of delay to LL reward. Error bars indicate SEM.