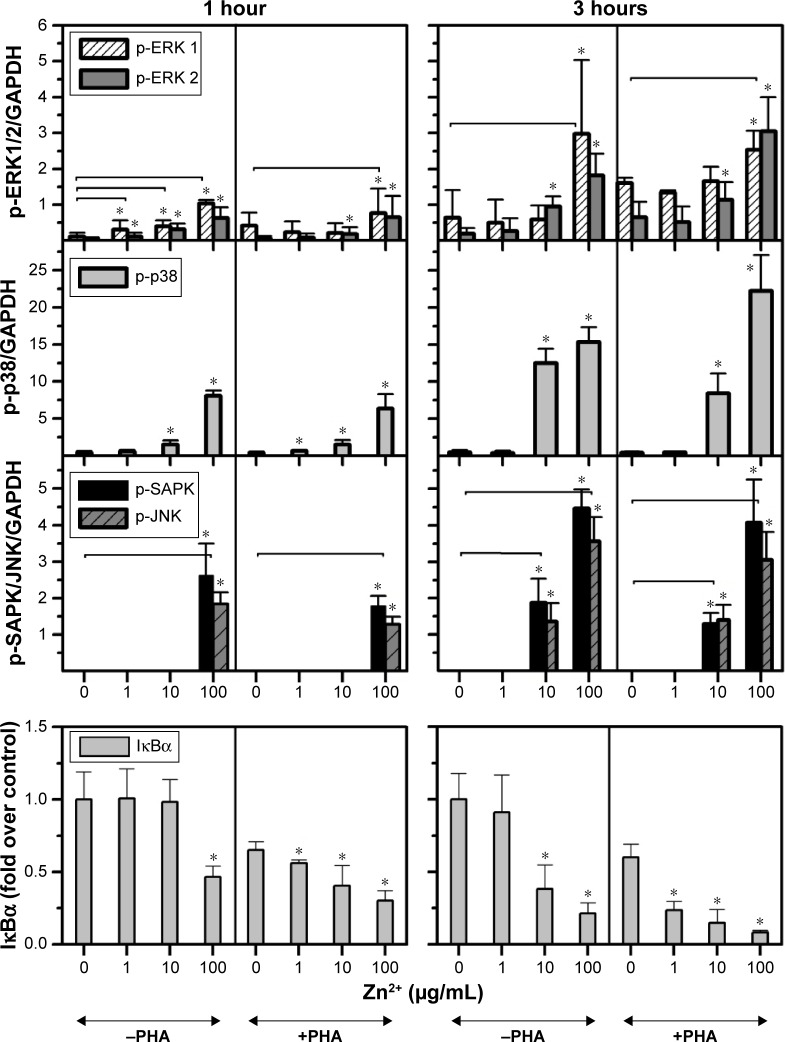
Figure 2.
Influence of the Zn2+ ion concentration on the activation of MAPK and NFκB in Jurkat cells.
Notes: The influence of ion release on the toxicity induced by ZnO nanoparticles was studied by incubating Jurkat cells, prestimulated (+PHA) or not (−PHA) with PHA, with three different concentrations of ZnCl2 salt as the source of Zn2+ ions (1, 10, and 100 μg/mL), and measuring the activation of ERK (1,2), p38, SAPK/JNK, and the NFκB pathways at 1 and 3 hours. *Statistically significant difference (P<0.05) in the level of protein compared with the control (untreated sample). The horizontal lines represent the treated samples that are statistically different from the control sample for both proteins studied.
Abbreviations: ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IκBα, NFκB inhibitor; JNK, c-Jun amino-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of the activated B-cell; PHA, phytohemagglutinin; SAPK, stress-activated protein kinase.