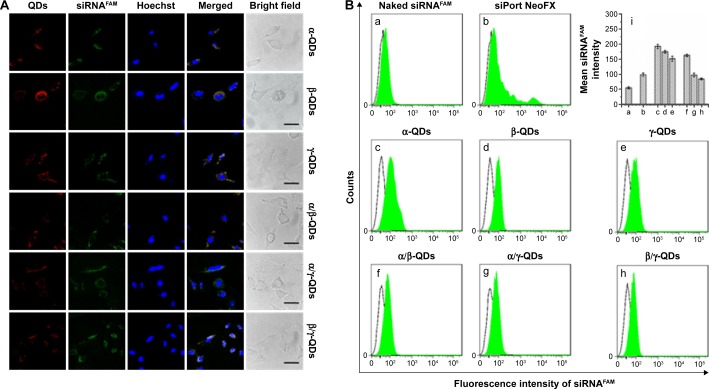
Figure 5.
siRNA transfection efficacy of QD nanocarriers.
Notes: (A) Intracellular uptake of siRNAFAM complexes transported by QD nanocarriers: rows show α-QDs, β-QDs, γ-QDs, α/β-QDs, α/γ-QDs, and β/γ-QDs after incubation with A549 cells for 3 hours and imaging by confocal laser scanning microscopy. QDs (red) and siRNA (green) were accumulated in the cytoplasm, and QDs were colocalized with siRNA. siRNA concentration: 50 nM. siRNA:QDs =1:1. (B) Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity of intracellular siRNAFAM transported by QD nanocarriers using flow cytometry: (a) naked siRNAFAM (negative control), (b) commercial siRNA carrier siPort NeoFX (positive control), (c) α-QDs, (d) β-QDs, (e) γ-QDs, (f) α/β-QDs, (g) α/γ-QDs, and (h) β/γ-QDs. (i) Mean siRNA intensities of samples (a–h).
Abbreviations: QD, quantum dot; siRNA, small interfering RNA.