Figure 1. AR156 pretreatment induces ISR to Pst DC3000 in Col-0 plants.
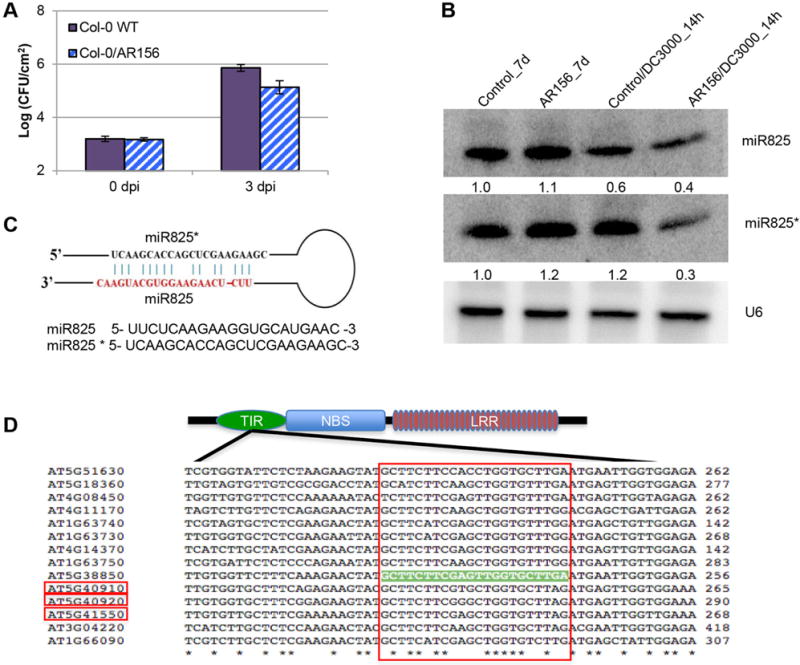
(A) Induction of systemic resistance to Pst DC3000 in Arabidopsis Col-0 plants by Bacillus cereus AR156. Plants are treated with AR156 at 5 × 107 CFU/ml and 0.85% NaCl for 7 days, respectively. Leaves are spray inoculated with Pst DC3000 cell suspension at 1 × 108 CFU/mL concentration. ISR is measured by counting colonies on plates 3 days after inoculation (dpi). (B) Expression of miR825 and miR825* in different treatments is examined by Northern blotting. Plants pre-treated with AR156 at 5 × 107 CFU/ml and 0.85% NaCl for 7 days, respectively. Leaves are spray inoculated with Pst DC3000 cell suspension at 1 × 108 CFU/ml concentration. Total RNA is extracted from leaves with line numbers and time points indicated. RNA blots are hybridized with DNA oligonucleotide probes complementary to the indicated miRNAs. U6 is used as a loading control. (C) Predicted secondary stem loop structure for miR825 and miR825* with mature miRNA sequences indicated. (D) Nucleotide sequences targeted by miR825* are aligned to corresponding genes, with the TIR-NBS-LRR gene structure depicted at the top. TIR: the toll-interleukin-like receptor domain; NBS: the nucleotide binding site domain; LRR: the leucine-rich repeat domain. Red boxes on gene IDs represent these genes that are validated by using real-time PCR in this study. The big red box shows the predicted target region, with the target site on AT5G38850 highlighted in light green. “*” represents conserved nucleotide.
