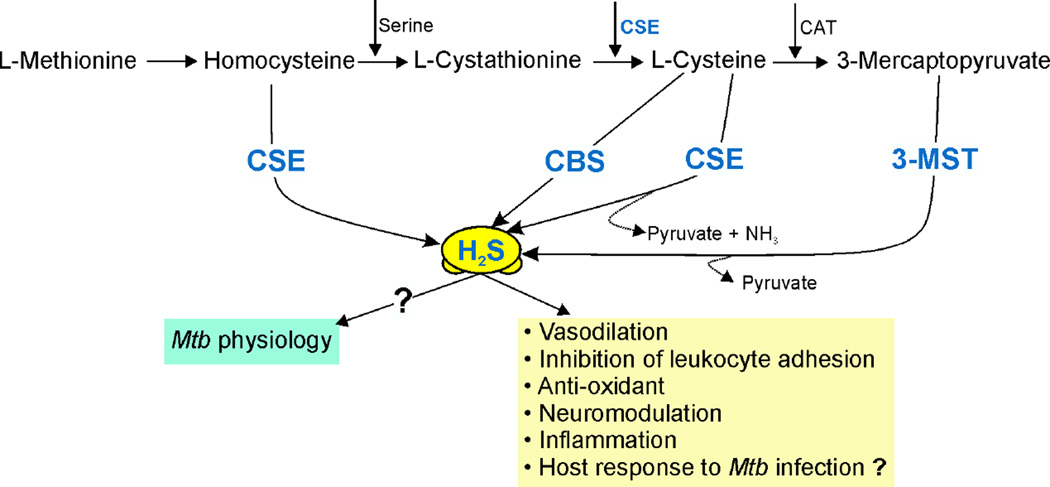
Figure 5. Schematic illustration of endogenous H2S production and functions.
H2S is produced endogenously by cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS), cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST). CBS and CSE use L-cysteine as the primary substrate with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate as a cofactor. H2S formation through 3-MST is downstream of cysteine aminotransferase (CAT), which catalyzes the reaction of L-cysteine with α-ketoglutarate leading to the formation of 3-mercaptopyruvate, the substrate used by 3-MST to form H2S and pyruvate. H2S is important for numerous physiological responses including vasodilation, neuromodulation, and inflammation and can also act as an anti-oxidant.