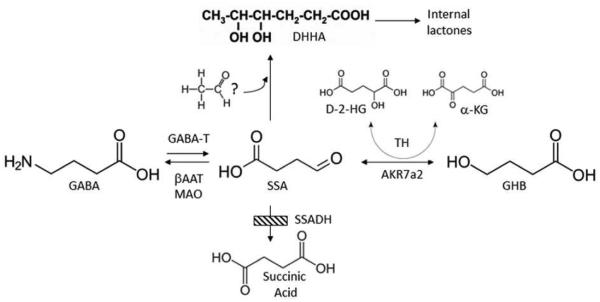
Fig. 2. GABA metabolism and SSADHD.
GABA normally interconverts to succinic semialdehyde via GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) activity, and subsequently forms succinic acid via succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH), the defect in SSADH deficiency (SSADHD; cross-hatched box). Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB; whose formation is catalyzed by aldo-keto reductase 7a2, AKR7a2), D-2-hydroxyglutaric acid (D-2-HG; the formation of which is catalyzed by nicotinamide-independent D-2-hydroxyglutaric transhydrogenase (TH)), SSA and 4,5-dihydroxyhexanoic acid (DHHA; possibly derived from SSA condensation with an “activated” two carbon species, but unproven) are increased in patient body fluids. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) and β-alanine aminotransferase (βAAT) can also metabolize GABA.