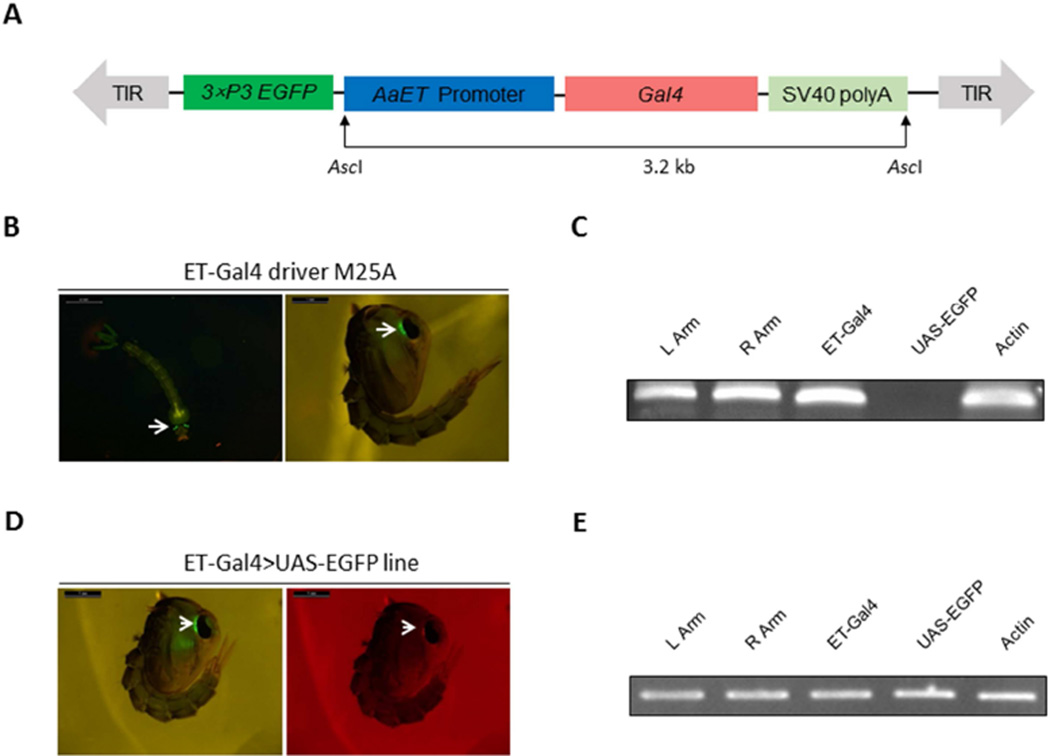
Figure 2.
A–C. Schematic representation of the ET-Gal4 vector used in germ-line transformation and characterization of the Ae. aegypti ET-Gal4 driver line. (A) Schematic representation of the ET-Gal4 vector. The ET-Gal4 vector contains the promoter region of the ET gene placed upstream of the Gal4 coding sequence. The EGFP marker gene is under the control of the 3×P3 promoter. (B) Expression of the EGFP marker in the M25A ET-Gal4 driver line. (C) Genomic PCR analysis showing integration of the ET-Gal4 cassette in the genome of the Ae. aegypti M25A ET-Gal4 driver line. Primers were specific to the left arm of the piggyBac vector (L Arm), the right arm of the piggyBac vector (R Arm), the Gal4 transgene (ET-Gal4), and the EGFP transgene (UAS-EGFP). PCR analysis of Actin acted as a positive control (Actin). D–E. Characterization of the ET-Gal4>UAS-EGFP hybrid line. (D) Both eye-specific selectable markers were present in the eyes of hybrid pupae—EGFP and DsRed. (E) PCR analysis demonstrated integration of the ET-Gal4 and UAS-EGFP cassettes in the Ae. aegypti genome. Photos were obtained using a Leica M165FC fluorescent stereomicroscope equipped with GFP-B filter and LAS V4.0 software. Scale bar: 1mm.