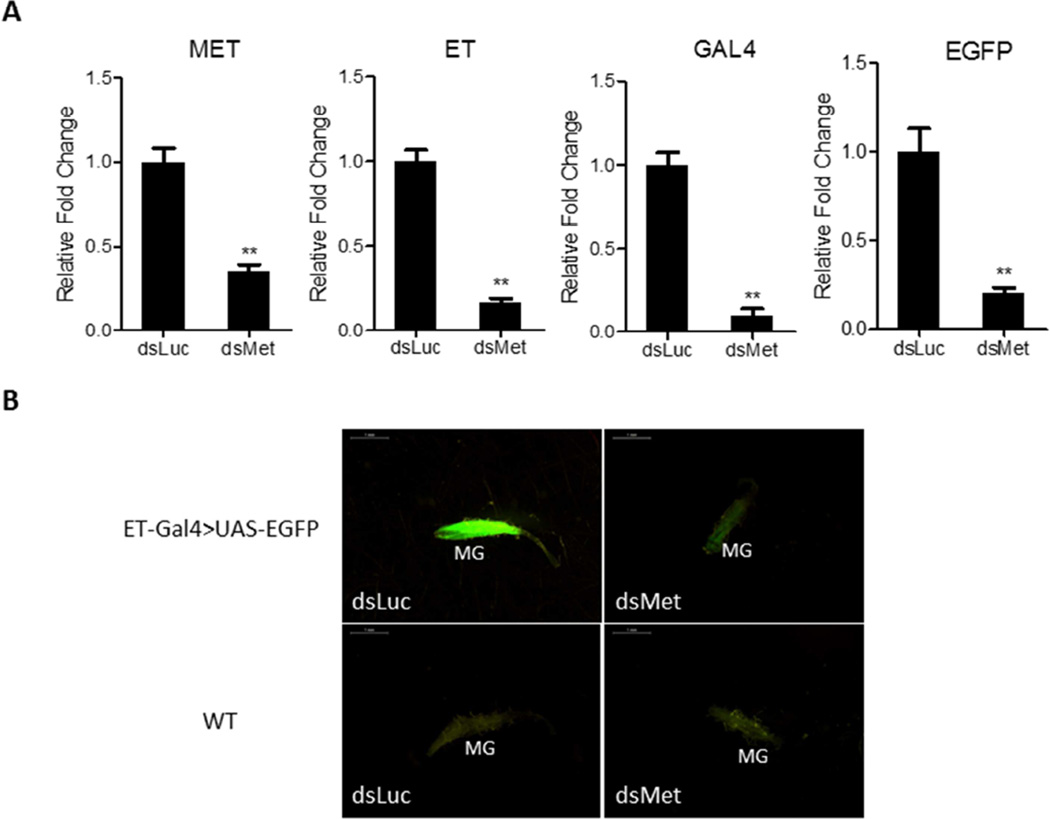
Figure 5.
Depletion of Met by RNAi results in inhibitory effects on the expression of endogenous ET and ET-Gal4>UAS-EGFP transgene. (A) Knockdown of Met by RNAi results in reduced transcript levels of endogenous ET and ET-Gal4>UAS-EGFP transgenes. The abundance of dsRNA-injected samples is represented as 1.0, with corresponding adjustments for other time points. Values represent average ± s.e.m. from three combined biological replicates. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (t-test) (B) The EGFP signal was significantly reduced in midguts (MG) of dsMet-treated female mosquitoes compared with dsLuc-treated female mosquitoes. WT mosquitoes treated with dsLuc or dsMet served as negative controls. Images were obtained using a Leica M165FC fluorescent stereomicroscope with LAS V4.0 software. Scale bar: 1 mm.