Fig. 10.
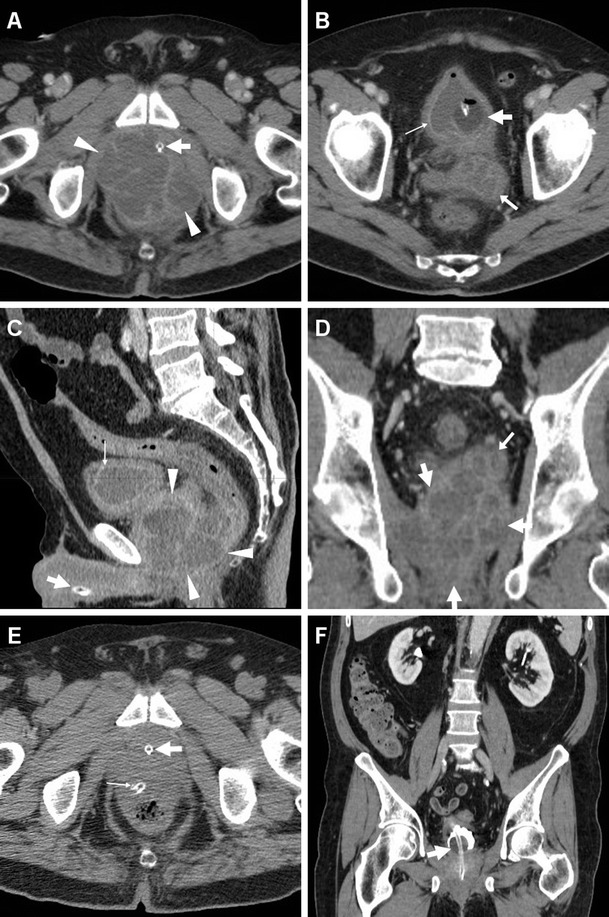
Large prostatic abscess from ESBL-positive Escherichia coli infection in a 61-year-old man with previous chemo- and radiotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, fever (38 °C), dysuria, pelvic pain and enlarged tender prostate at digital rectal examination. Multiplanar CT images (a–d) showed marked prostatic enlargement by confluent nonenhancing hypoattenuating (17–19 HU) regions, with peripheral and septal enhancement (arrowheads). The prostatic infection also involved the left seminal vesicle (arrows in b, d), displaced upwards of the urinary bladder, with mild circumferential mural thickening and mucosal hyperenhancement (thin arrows) consistent with UTI. After transperineal evacuation (e), follow-up CT urography (f) confirmed persistent resolution of the abscess [Partially reproduced from Open Access Ref. [47]]
