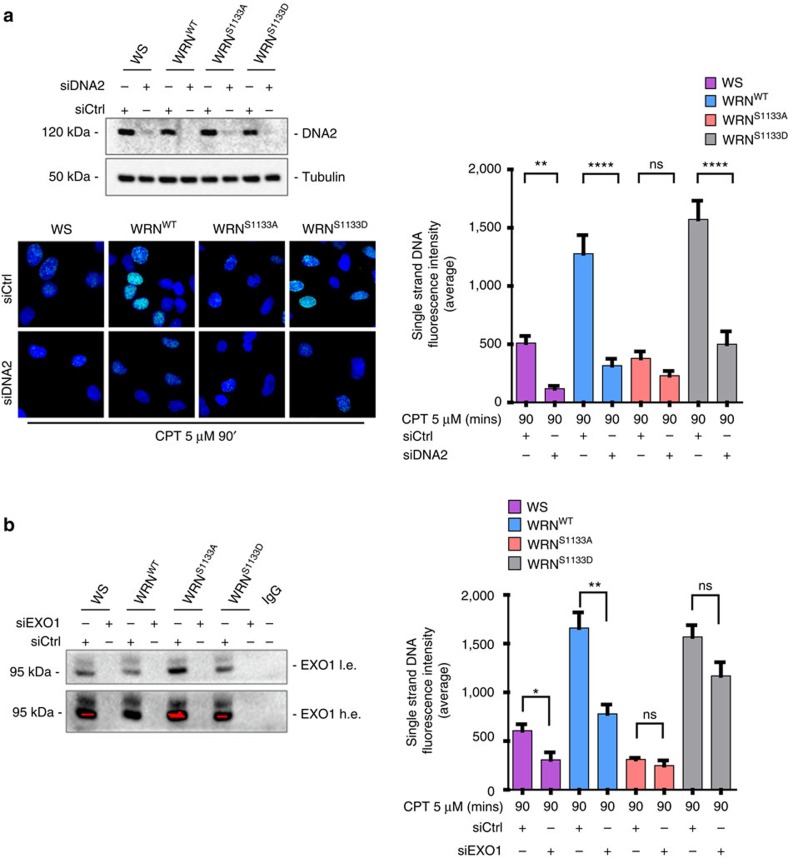
Figure 4. CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of WRN at S1133 affects the WRN helicase-DNA2-dependent pathway of end resection.
(a) Loss of WRN phosphorylation impinges on DNA2-dependent end resection. Western blotting shows depletion of DNA2 in cells expressing WRN wild type or its phosphorylation mutants. Whole-cell extracts were prepared at 48 h after transfection with DNA2 siRNA. Representative images of control (Ctrl)-depleted or DNA2-depleted cells treated with CPT and immunostained for IdU/ssDNA are shown. The graph shows the mean intensity of IdU/ssDNA staining in cells treated or not with the DNA2 siRNA. The intensity of the anti-IdU immunofluorescence was measured in two independent experiments (n=100, each biological replicate), data are presented as mean±s.e.m. (b) Loss of WRN S1133 phosphorylation affects EXO1-mediated degradation. Western blotting shows depletion of EXO1 in cells expressing WRN wild type or its phosphorylation mutants, or no WRN (WS). Whole-cell extracts were prepared at 48 h after transfection with EXO1 siRNA and immunoprecipitated with an anti-EXO1 antibody, followed by WB with the same antibody. End resection was evaluated by the IdU/ssDNA assay. The graph shows the mean intensity of ssDNA staining for single nuclei quantitated from two independent experiments (n=100, each biological replicate), data are presented as mean±s.e.m. Statistical analysis was performed by the analysis of variance test (****P<0.0001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05; NS, not significant).