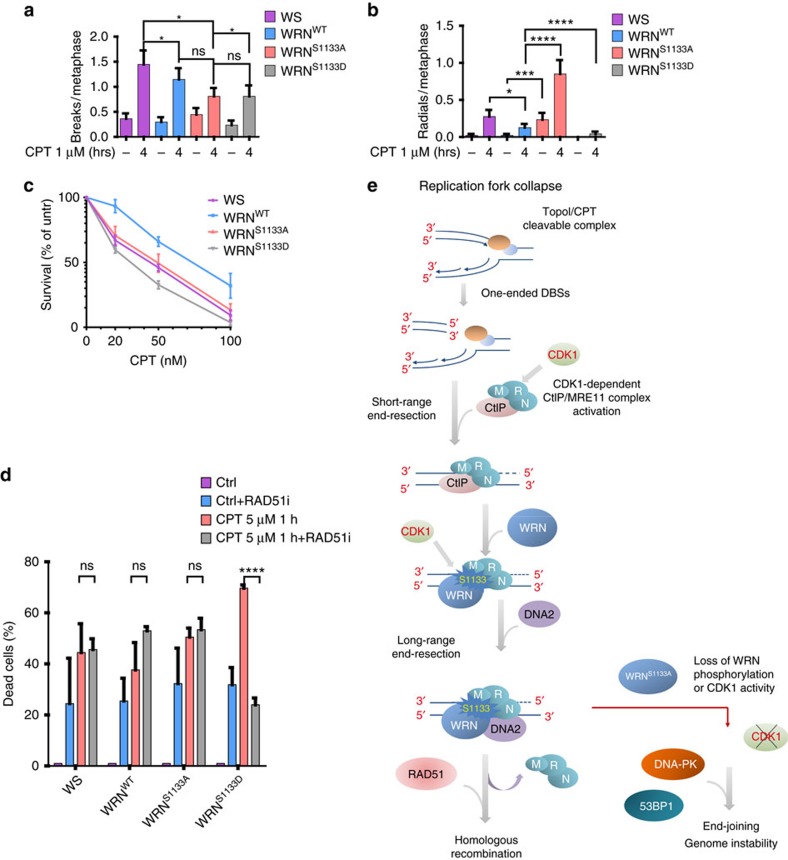
Figure 8. CDK-dependent phosphorylation of WRN is required for genome integrity and survival in response to replication-dependent DSBs.
(a,b) Graphs show the average number per cell of the indicated chromosomal aberrations in WS and the different WS-complemented cells. Cells were treated with 1 μM CPT 4 h followed by 24 h of recovery in drug-free medium before collecting. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. of three independent experiments (*P<0.05; ***P<0.001; ****P<0,0001; NS, not significant, analysis of variance (ANOVA) test; n=150). (c) Analysis of clonogenic survival. Cells expressing the wild-type or the two phosphomutant form of WRN were treated with CPT for 24 h at the indicated doses and the number of colonies for each experimental point was recorded and expressed as a percentage of the untreated control. Data are mean±s.e.m. from two independent experiments. (d) RAD51 inhibition in WRN phosphomimetic mutant expressing cells modulates sensitivity to CPT. Cells were treated with CPT for 1 h, as indicated. The B01 RAD51 inhibitor was added before CPT treatment, and then cells were recovered for 18 h in the continuous presence or not of the inhibitor before assessing cell death by LIVE/DEAD assay. Data are presented as percentage of cell death and are mean values from three independent experiments (****P<0.0001; ***P<0.001, ANOVA test; NS, not significant; n=3). (e) Proposed model of CDK-dependent regulation of WRN in the repair of DSBs at the replication fork (see text for details).