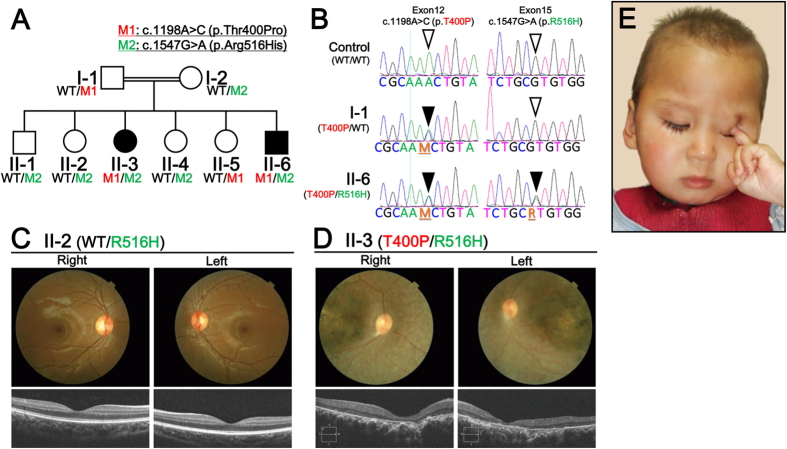
Figure 1. Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and Clinical Diagnosis.
(A) Recessive patterning of a consanguineous LCA family was performed and compound heterozygous mutations were identified. Whole exome sequencing was performed and two point mutations in CCT2 were found, c.1198A > C and c.1547G > A, which resulted in following substitutions: p.Thr400Pro (p.T400P) and p.Arg516His (p.R516H), respectively. (B) CCT2 gene mutations and corresponding amino acid substitutions in the CCTβ protein were identified. Point mutations in Exon 12 (c.1198A > C) and Exon 15 (c.1547G > A) resulted in the CCTβ missense changes, T400P and R516H, respectively. (C) Clinical evaluations of the non-affected individual, II-2. Upper panel: Color fundus photographs showed a normal retina. Lower Panel: An OCT examination also showed a normal retina. (D) Clinical evaluations of the affected individual, II-3. Upper panel: Color fundus photographs showed severe degenerative changes. The optic disc was pale and the retinal blood vessels were attenuated. A maculopathy with chorioretinal atrophy and aggregation of the pigment were also observed. Lower panel: An OCT examination showed the thinning and disorganization of the retina. Both c.1198A > C (M1 in red) and c.1547G > A (M2 in green)-carrying individuals (e.g., II-3 and II-6, respectively) exhibited retinal dystrophy and a macular degeneration phenotypes. (E) Facial and behavioral features of the oculodigital phenomenon (eye poking) and sunken eyes (enophthalmos) of the affected individual, II-6.