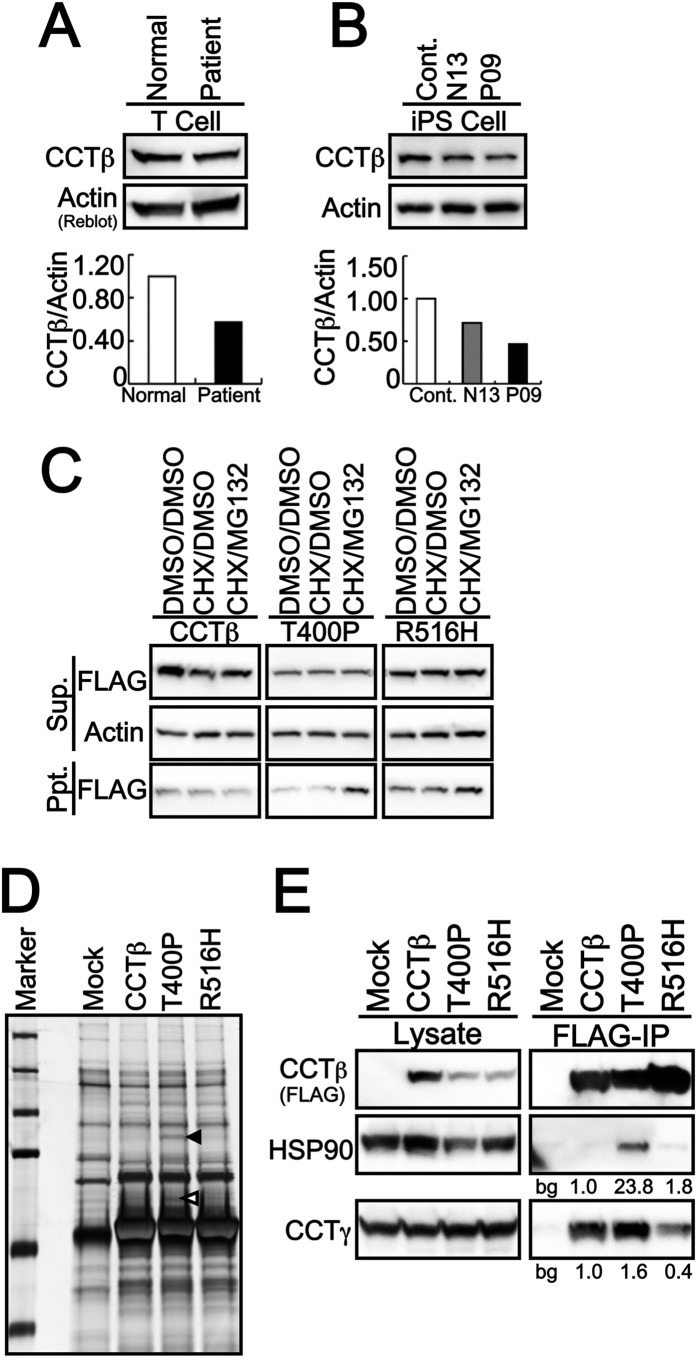
Figure 3. Intracellular Dynamics of CCTβ and its LCA-causing mutants.
Expression levels of CCTβ protein in patient-derived T cells (A) and iPSCs (B) were analyzed by WB. Lower levels of CCTβ were detected in patient-derived T cells and iPSCs (P09) compared with the parental control iPSCs (N13) and wild-type CCTβ-carrying control iPCSs (Cont.). (C) Intracellular protein stability was monitored using the proteasomal degradation inhibitor, MG132, and protein synthesis was abolished with cychloheximide (CHX) treatment for 3 h. Cytosolic protein levels of T400P were lower than R516H and wild-type CCTβ. The insolubility of T400P and R516H is predicted to contribute to the degradation observed. Sup., supernatant fraction; Ppt., Precipitated fraction. (D) Each FLAG-tagged transfected sample was immunoprecipitated (IP) and subjected to WB and silver staining. Two distinct binding bands were observed for the T400P variant (indicated with a black arrowhead and the white arrowhead respectively). These two bands were digested with trypsin by an in-gel method and was subsequently identified as containing HSP90 (black arrowhead) and CCTγ (white arrowhead) by LC/MS/MS. (E) Consistent with the MS analysis data, T400P exhibited a higher affinity for HSP90 and CCTγ in IP and WB assays. In contrast, R516H exhibited a lower affinity for CCTγ. Thus, these CCTβ variants appear to affect CCTγ during oligomerization of the CCT-chaperonin ring. The number labels in (E) indicate the fold-change in expression compared to wild-type HSP90 or wild-type CCTβ. Bg: background from mock (empty vector transfected) control.