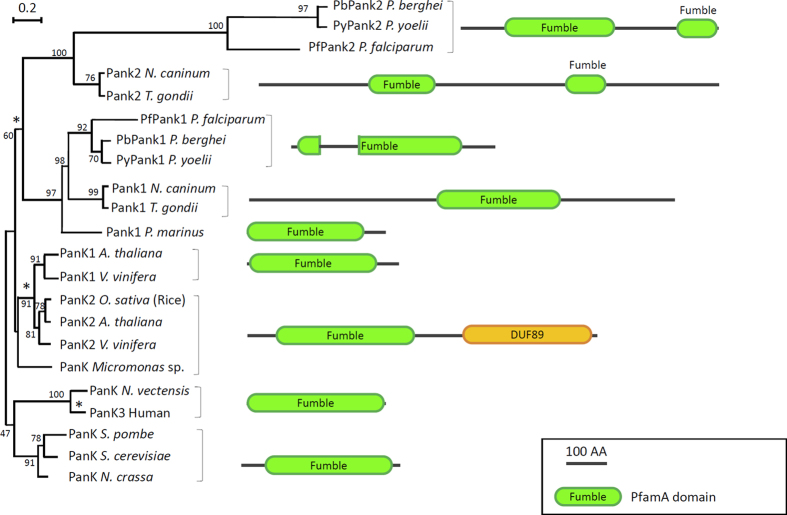
Figure 2. Sequence structure and evolution of Apicomplexan PanK1 and PanK2 proteins compared to confirmed pantothenate kinases.
Schematic diagram showing eukaryotic pantothenate kinase protein organization from plants, protists and algae that are closely related to human PanK3. Apicomplexan PanKs are shown with Plasmodium conserved PanK1 and PanK2 that resemble PanK1 and PanK2 from Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii, respectively. The phylogenetic analysis has been inferred by Maximum Likelihood, using Muscle and PhyML through phylogeny.fr “one click” option web interface. Scale bar indicates the number of substitution per site. Protein structures have been deduced from PfamA database and results from Pfam search engine. Star (*) indicate node where duplication of the PanK gene may have occurred during evolution of eukaryotes. The bootstrap values are shown next to the cluster of the tree.