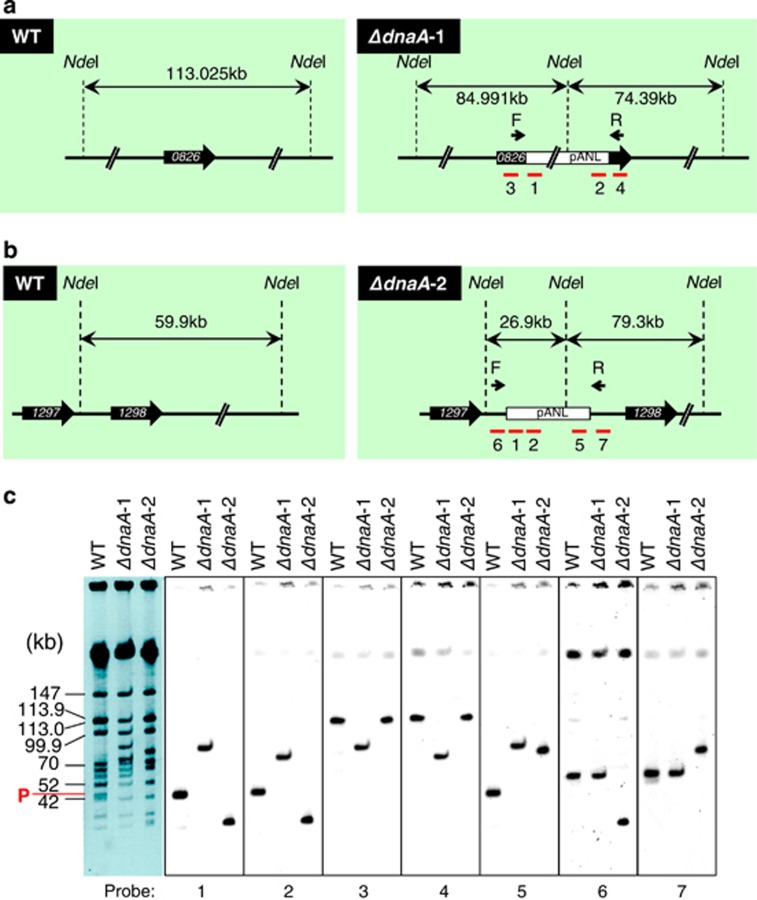
Figure 3.
Chromosomal insertion of plasmid pANL in dnaA disruptants of S. elongatus. Schematic representation of the region surrounding the plasmid insertion site in ΔdnaA-1 (a) and ΔdnaA-2 (b). Sizes of fragments digested with NdeI are indicated for WT (left) and dnaA disruptants (right) strains. Red bars with numbers indicate probes used for Southern blot hybridization in (c). The pANL plasmid was integrated into the middle of the Synpcc7942_0826 gene and downstream of the Synpcc7942_1297 gene in ΔdnaA-1 and ΔdnaA-2, respectively, and corresponded to new replication origins, as determined by Repli-seq. (c) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) pattern (left) and results of Southern hybridization with DNA probes specific to the plasmid (1, 2 and 5), Synpcc7942_0826 gene (3 and 4) and intergenic region between Synpcc7942_1297 and Synpcc7942_1298 (6 and 7), as shown in (a) and (b). Chromosome fragment sizes and plasmid fragments (P; 46 kb) are indicated to the left of PFGE image.