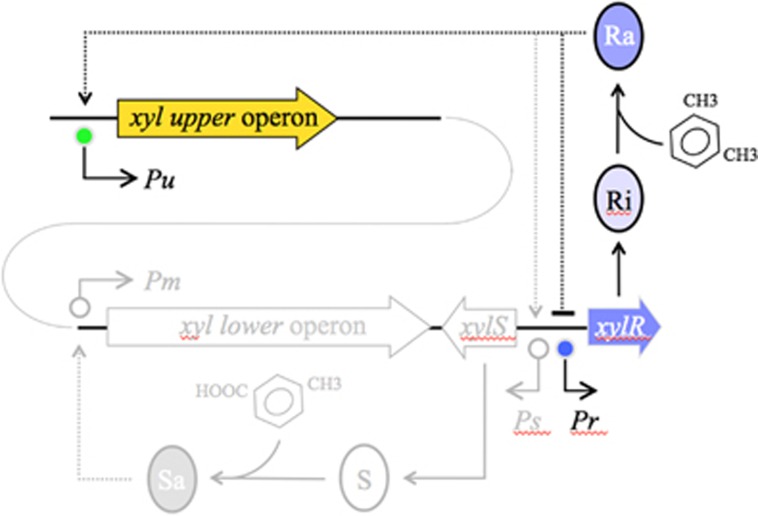
Figure 1.
Organization of the TOL network of the TOL plasmid pWW0 of P. putida mt-2. The TOL pathway encoded by plasmid pWW0 consists of two different operons: the upper operon, the products of which transform m-xylene into 3-methylbenzoate, and the lower operon that produces enzymes for further metabolism of this compound into TCA cycle intermediates. XylR and XylS are the transcriptional regulators that control expression of either operon. The master regulatory gene xylR is encoded in a location adjacent to the end of the meta operon and is expressed from the Pr promoter. XylR is produced in an inactive form (Ri) that, in the presence of the pathway substrate (m-xylene) changes to an active form (Ra). Ra then activates both Pu and Ps, triggering expression of the upper pathway and XylS, respectively. At the same time, Ra acts as repressor of its transcription, thereby decreasing its own expression. The part of the network under study is highlighted in colour, the rest is faded. Operons and regulatory elements not to scale.