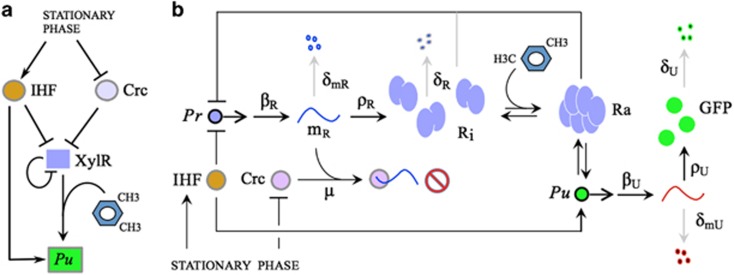
Figure 2.
The Pr/XylR/Pu node and formalization of regulatory interactions. (a) Basic interactions between the Pu promoter, its cognate regulator XylR and the global regulators IHF and Crc whose levels are modulated by growth state. (b) Biochemical reactions involved in the upper route of the TOL pathway. We take into account transcription from the Pr and Pu promoters (with rates βR and βU, respectively), translation of the corresponding mRNAs (with rates ρR and ρU), and degradation of the molecular species: mRNAs (with degradation rates δmR and δmU) and proteins (with rates δR and δU). Translational repression of xylR mRNA (mR) by Crc is described by the effective association rate constant μ. We also consider, sketched as double arrows, the activation (mediated by m-xylene) and inactivation reactions of XylR, as well as the binding/unbinding reactions of active XylR (Ra) to the Pu promoter. A detailed description of the model is provided in Supplementary Information, and the values of the reaction rates specified in Table 1.