FIGURE 3.
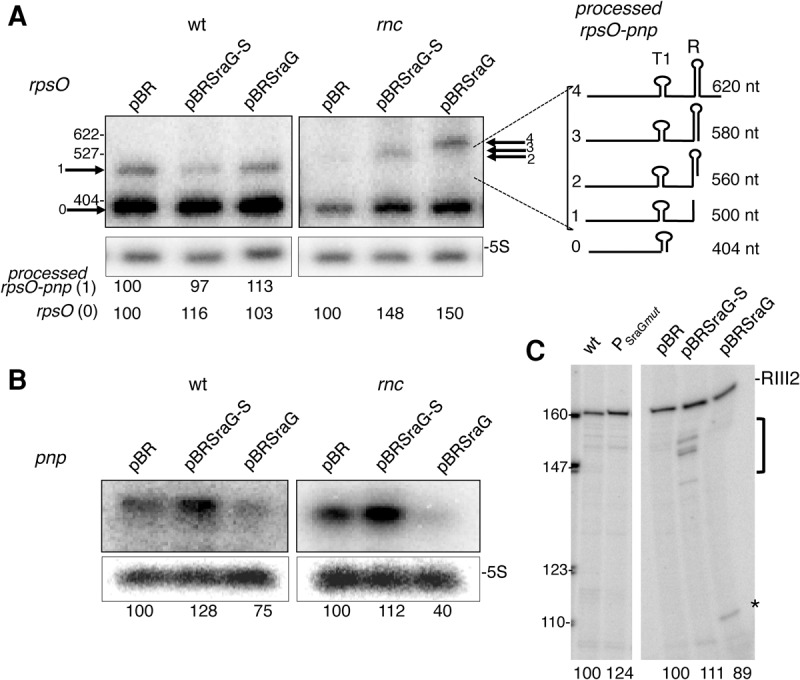
Overexpression of SraG affects the abundance of pnp, but not rpsO mRNAs. Northern blot analysis of rpsO (A) and pnp (B) RNA in FF4 (wt) and FF19 (rnc) containing the pBRplac (pBR), pBR-SraG (pSraG), and pBR-SraG short (pSraG-S) plasmids. Expression of SraG was induced by adding IPTG (100 µM) for 7 min. Radioactivity corresponding to each transcript was quantified and normalized relative to 5S and compared to the strain carrying the empty pBRplac plasmid. The mean value (in arbitrary units) of three independent experiments relative to the corresponding pBR containing cells is indicated below the gel. The Northern blot showing pnp detection in the rnc mutant was underexposed compared to wt to allow comparison. In A, the arrows indicate the various processed forms containing rpsO derived from the dicistronic transcript, which are numbered according to their size and schematically represented on the right side of the Northern blot. Cleavage by RNase III on the left side of the R secondary structure (RIII1 site) generated rpsO-pnp processed form 1 is detected in the wt strain. In the rnc strain, longer transcripts (2,3,4) are detected corresponding to cleavages within or downstream from the R secondary structure. (C) Total RNA from N3433 (wt), N3433 lacking SraG (mutation in SraG promoter PSraGmut) (left panel), and FF4 transformed with pSraG, pSraG-S, and empty pBRplac vector (same RNA preparations as in A and B) were used as templates for reverse transcription primed with the radiolabeled RNX1 primer. Reverse transcripts corresponding to the RNase III2 cleavage site (Fig. 1) are indicated, the asterisk (*) and bracket indicate other reverse transcriptase stops. Radioactivity corresponding to RNase III-processed pnp transcript was quantified and compared to the wt strain without plasmid or carrying the empty pBRplac plasmid. These values (in arbitrary units) are indicated below the gel.
