Figure 1.
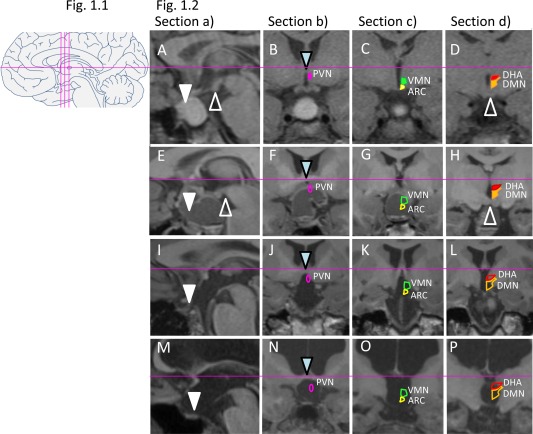
1.1: Schematic overview of standard brain sections for assessment of lesions (midline sagittal: a; three coronal sections: b, c, d). 1.2: MRI standard brain sections and HLS in four patients following craniopharyngioma resection. Solid shapes of nuclei indicate intact structures, while open shapes indicate lesions. A‐D: Male patient presenting with residual intra‐/suprasellar tumor (A), while PVN (pink in B), ARC (yellow in C), and VMN (green in C), as well as DHA (red in D) and DMN (orange in D), are still intact. HLS: 0. BMI z‐score at surgery ‐1.11 (age 11 years), BMI z‐score 3 years post‐surgery ‐0.6. (E‐H): Female patient showing a residual suprasellar/hypothalamic cystic lesion and defect of the anterior and medial hypothalamus. HLS: 3. BMI z‐score at surgery 0.09 (age 14 years), BMI z‐score 2 years post‐surgery 0.13. (I‐L): Female patient with BMI z‐score at surgery 2.22 (age 7 years) presenting with large postoperative lesion affecting the floor of the third ventricle and whole hypothalamus. HLS: 5. BMI z‐score 3 years post‐surgery 2.28. (M‐P): Female patient presenting with large lesion, hydrocephalus, and absence of pituitary, optic chiasm, pituitary stalk, floor of third ventricle, PVN, ARC, VMN, DHA, and DMN. HLS: 7. BMI z‐score at surgery 0.71 (age 11 years), BMI z‐score 2 years post‐surgery 1.87. Triangles point to landmarks of orientation: sella (white), mammillary bodies (white open), and anterior commissure (blue).
