Figure 5. PPARα-PGC-1α-mediated antioxidant pathway, oxidative stress and skeletal muscle degeneration in ATGL-KO mice.
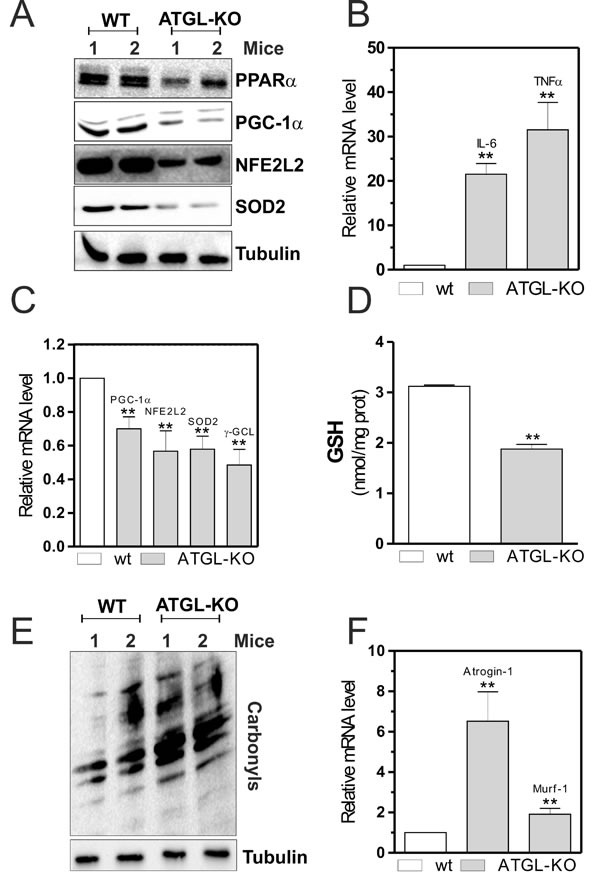
A. Skeletal muscle of two wild type (WT) and two ATGL-KO mice was homogenized and 20 μg of total proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis of PPARα, PGC-1α, NFE2L2 and SOD2. Tubulin was used as loading control. B., C. Total RNA was isolated from skeletal muscle of two WT and two ATGL-KO mice, and relative mRNA levels of IL-6, TNFα, PGC-1α, NFE2L2, SOD2 and -GCL were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3, **p < 0.001 vs. WT mice). D. GSH content of WT and ATGL-KO mice was assayed by HPLC. Data are expressed as nmoles of GSH/mg of proteins and reported as means ± S.D. (n = 3, **p < 0.001 vs. WT mice). E. Twenty μg of total proteins were derivatized with DNP and carbonylation was detected by Western blot with DNP antibody. Tubulin was used as loading control. All the immunoblots reported are from one experiment representative of five that gave similar results. F. Total RNA was isolated from skeletal muscle of WT and ATGL-KO mice, and relative mRNA levels of Atrogin-1 and Murf-1 were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3, **p < 0.001 vs. WT mice).
