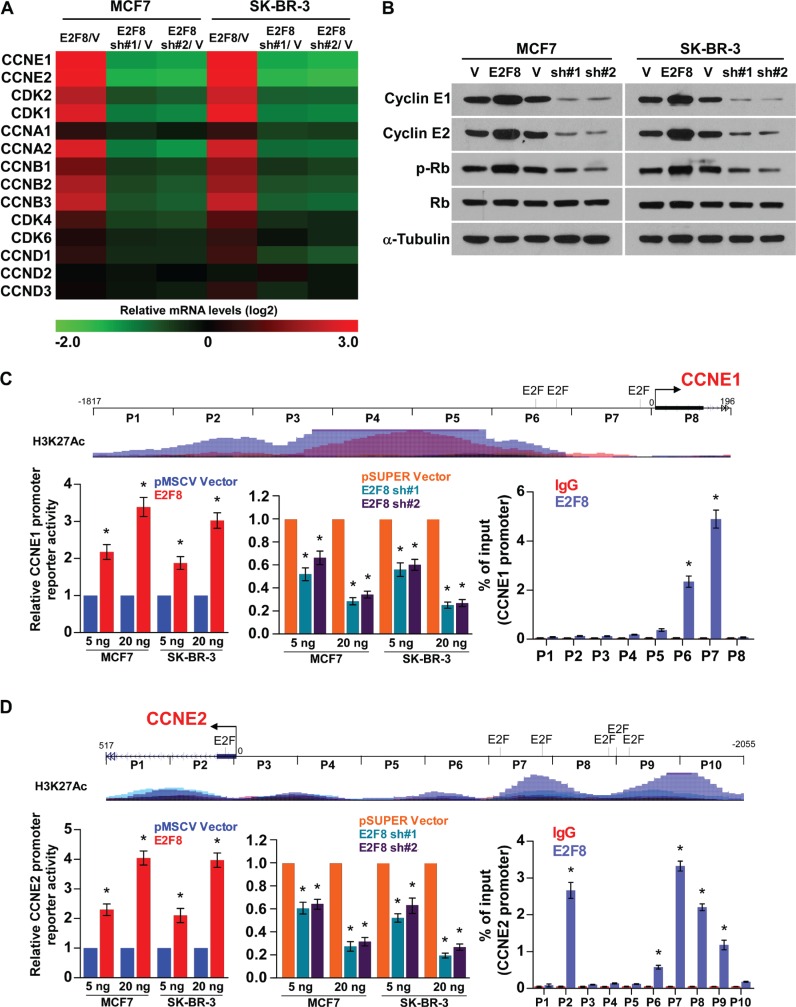
Figure 6. E2F8 directly upregulates the promoter activities of cyclin E1 and cyclin E2.
(A) Real-time PCR analysis of cell cycle-related genes mRNA expression in the indicated cells. Gene expression levels were normalized to GAPDH. The pseudocolours represent the intensity scale of E2F8 versus pMSCV vector (V) or E2F8 sh#1/2 versus pSUPER vector (V), generated by log2 transformation. (B) Western blotting analysis of cyclin E1, cyclin E2, phosphorylated Rb (p-Rb) and total Rb protein expression in the indicated cells; α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (C and D) Upper panel: Schematic illustration of ChIP PCR fragments for the indicated nucleotide regions of the CCNE1 (C) and CCNE2 (D) promoters. Multiple typical response elements of E2F transcription factor were predicted using the ConSite program. H3K27Ac enrichment, indicating high transcription activity, is observed in the promoter elements according to Genome Browser Gateway website. Left panel: Luciferase activity assays in MCF7 and SK-BR-3 cells showed transactivation of the CCNE1 and CCNE2 promoters by E2F8 overexpression and repression by E2F8 silencing. Right panel: ChIP enrichment assay confirms that E2F8 binds to the predicted promoter site of CCNE1 and CCNE2; IgG was used as a negative control. Results were evaluated from three independent experiments, *P < 0.05.