Figure 3. Oral administration of EGFR inhibitors reduced HFD-induced inflammation and ROS production in the kidneys of ApoE−/− mice.
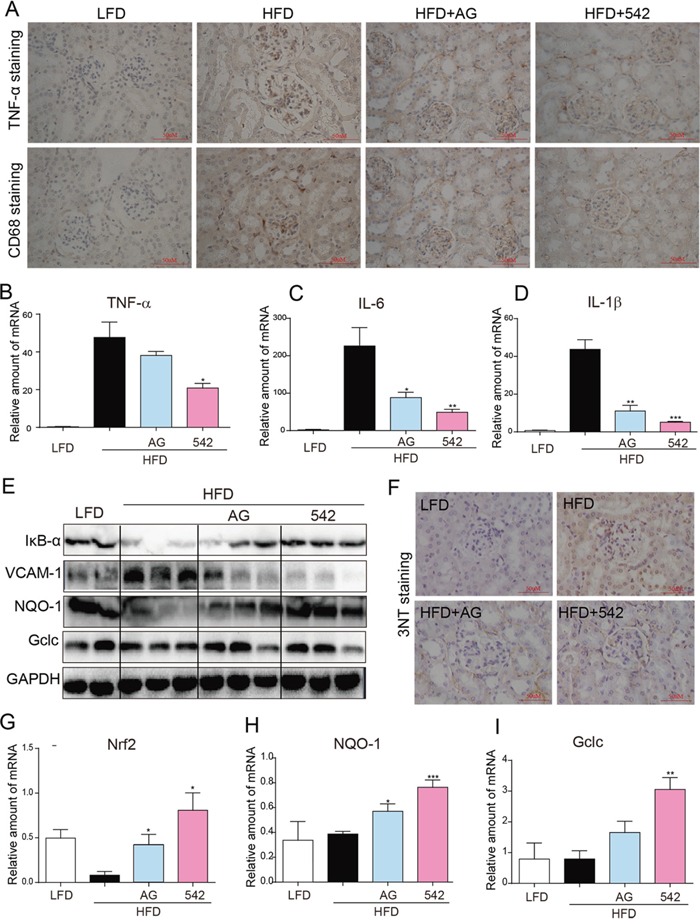
A. The administration of 542 for 2 months significantly reduced HFD-induced increases of kidney inflammation, including expression of TNF-α, and macrophage infiltration as characterized by CD68 staining. B-D. 542 also reduced the mRNA expression of TNF-α (B) and other inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 (C) and IL-1β (D). E. Administration of 542 also inhibited the degradation of IκB and expression of adhesion factors VCAM-1. F-I. 542 administration reduced the HFD-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Immunohistochemistry revealed that 542 decreased HFD-induced 3-NT (F) and RT-qPCR showed 542 increased mRNA levels of antioxidants, such as Nrf2 (G), NQO-1 (H) and Gclc (I), as well as the protein levels of antioxidant proteins NQO-1 and Gclc (E). (n=7/8; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; vs. HFD group; LFD, low-fat diet; HFD, high-fat diet)
