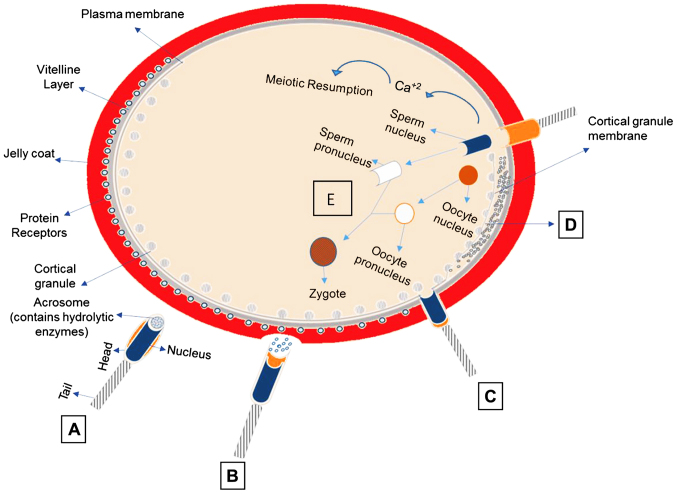
Figure 1.
The events taking place in fertilization. (A) Sperm preparation-capacitation: Molecules (resact, speract) secreted from the oocyte, orient and stimulate sperm (guanylate cyclase). (B) Acrosome reaction: release of hydrolytic enzymes. The sperm via SED1 protein is connected to ZP3. (C) Fusion of sperm with plasma membrane of the oocyte: sperm pre-acrosin binds to ZP2. Proteins of sperm IZUMO, ADAMs 1, ADAMs 2, ADAMs 3 and CRISP1 bind to receptors on the oocyte (Juno, integrins, CD9, CD81). Other molecules identified playing role in gamete fusion are: Trypsin-like acrosin, spermosin, SPAM1, HYAL5, ACE3. (D) Cortical Reaction: Ca+2 release/wave of Ca+2 and formation of fertilization cone. Enzymes released by cortical granules, digest sperm receptors ZP2 and ZP3 (block of polyspermy). (E) Sperm chromatin decondensation to form male pronucleus: The oocyte nucleus completes the 2nd meiosis and eliminates the 2nd polar body.