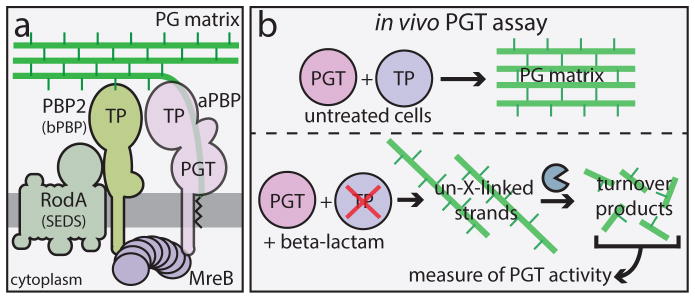
Fig. 1. The Rod system and an in vivo assay of peptidoglycan (PG) polymerase activity.
A. Diagram of the currently accepted model for PG biogenesis by the Rod system. Polymers of the actin-like MreB protein organize a complex of membrane proteins including RodA, PBP2, and an aPBP. Glycan polymerization and crosslinking by this complex is thought to be promoted primarily by the peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase (PGT) and transpeptidase (TP) activities of aPBPs with additional TP activity provided by PBP2. B. In untreated cells, PG polymerization and crosslinking by PGT and TP enzymes, respectively are tightly coupled to form the PG matrix (upper panel). When TP activity is inhibited by a beta-lactam, the polymerase working with the blocked TP continues to produce uncrosslinked glycans that are rapidly degraded into fragments that can be isolated and quantified as a measure of polymerase activity (lower panel).