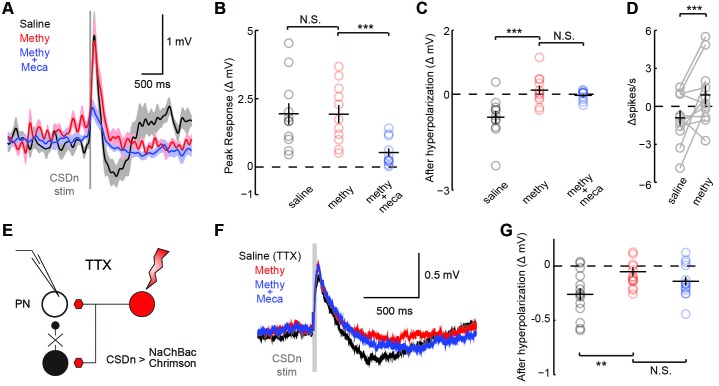
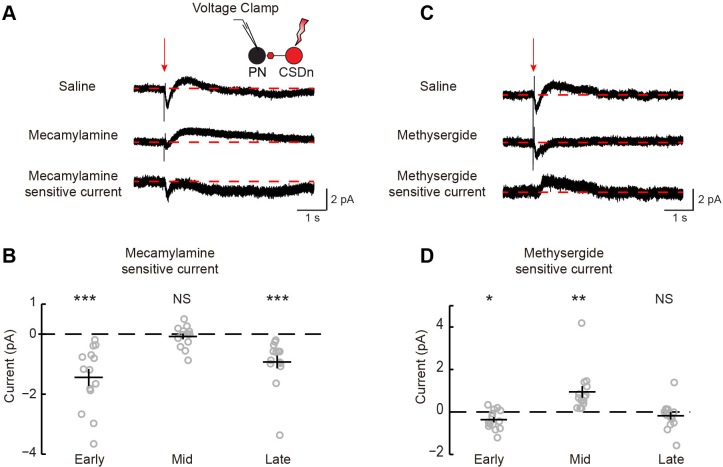
Figure 4. CSDn makes similar connections onto PNs as LNs.
(A) PNs were held at −60 mV. Stimulation of the CSDn depolarizes PNs briefly and results in a delayed hyperpolarization (gray trace, saline). (B) The early depolarization could not be blocked by methysergide (50 μM) but was blocked by mecamylamine (100 μM), ANOVA, n = 11, F = 27.6, p=1.77 × 10−6, saline vs methysergide p=0.99, methysergide vs methysergide plus mecamylamine p=8.67 × 10−6. (C) The delayed hyperpolarization was fully blocked by methysergide, while mecamylamine had no further effect on the delayed part of the response, ANOVA, n = 11, F = 13.32, p=0.0002, saline vs methysergide p=2.70 × 10−4, methysergide vs methysergide plus mecamylamine p=0.63. (D) PNs were depolarized to −30 mV to induce spiking and to amplify the effects of the hyperpolarization. At −30 mV CSDn stimulation significantly reduced PN firing, n = 11, p=0.031. (E) PNs were patched in saline containing TTX to block all activity in the brain. NaChBac and Chrimson were co-expressed in the CSDn to selectivity restore activity only in this neuron to probe monosynaptic connections with randomly selected PNs. (F) CSDn stimulation rapidly depolarized the PNs and then hyperpolarized them in TTX. (G) The hyperpolarization was blocked by methysergide, ANOVA, n = 14, F = 5.58, p=0.0096, saline (TTX) vs methysergide p=0.0072, methysergide vs methysergide plus mecamylamine p=0.35.