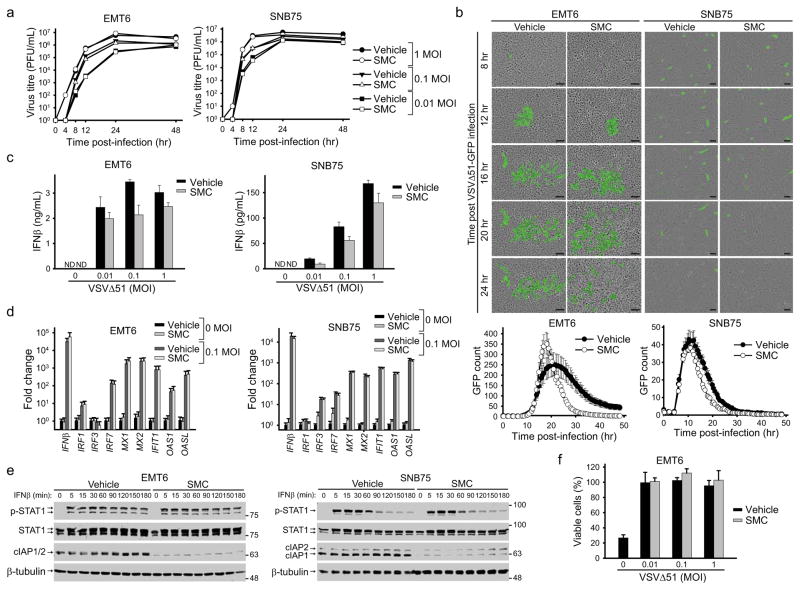
Figure 2. SMC treatment does not alter the antiviral response of cancer cells.
a, Cells were pretreated with vehicle or 5 μM LCL161 for 2 hr and infected with the indicated MOI of VSVΔ51. At indicated time points, virus titre was assessed by a standard plaque assay. Error bars, mean ± s.d. b, Cells were treated with vehicle or 5 μM LCL161 and infected with VSVΔ51-GFP (0.1 MOI). Cells were imaged every 30 minutes using the Incucyte Zoom. Images are representative of four experiments and graphs below images show the number of GFP signals detected at each time point was plotted. Error bars, mean ± s.d. n = 12. Scale bar, 100 μm. c, Cell culture supernatants from cells treated with vehicle or 5 μM LCL161 and indicated MOI of VSVΔ51 for 24 hr were processed for the presence of IFNβ by ELISA. Error bars, mean ± s.d. n = 3. d, Cells were treated with vehicle or 5 μM LCL161 and indicated MOI of VSVΔ51 for 20 hr. Cells were then processed for RT-qPCR to measure expression of virus and IFN stimulated gene transcripts indicated on the x-axis. Error bars, mean ± s.d. n = 3. e, Cells were pretreated with 5 μM LCL161 for 2 hr and subsequently stimulated with IFNβ for the indicated times. Total and phosphorylated STAT1 was measured by Western blot. f, EMT6 cells were treated with vehicle or 5 μM LCL161 and infected with the indicated MOI of VSVΔ51 for 20 hr. Media was exposed to UV light and then applied to uninfected cells. Cells were subsequently challenged with 1 MOI of wild-type VSV for 48 hr and the proportion of rescue of cell death from wild-type VSV was measured by an Alamar Blue viability assay. Error bars, mean ± s.d. n = 3. All figure panels: representative data from at least three independent experiments using biological replicates.