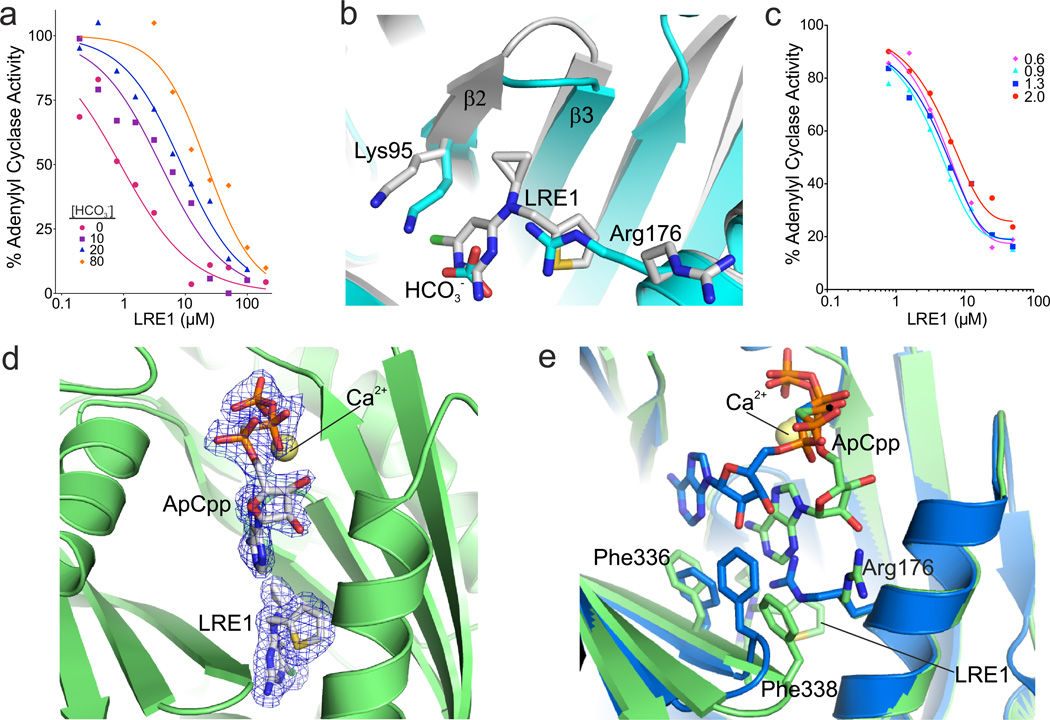
Fig. 4. Mechanistic characterization of sAC inhibition by LRE1.
(a) LRE1 is competitive with HCO3−. sAC activity, measured by RF-MSS in the presence of the indicated concentration of LRE1 and 1 mM ATP/5 mM MgCl2/5 mM CaCl2 with 0 (red); 10 (purple squares); 20 (blue triangles); or 80 (orange diamonds) mM NaHCO3. Data represent means of triplicate determinations of an experiment repeated twice. (b) Overlay of sAC/LRE1 (grey) with a sAC/bicarbonate complex (cyan, RMSD 0.3 Å5 for 352 Cα atoms). The ligands and the two key residues for bicarbonate binding are shown as sticks colored according to atom type. (c) LRE1 does not compete with ATP. sAC activity, measured by RF-MSS in the presence of the indicated concentration of LRE1 and either 0.6 (pink diamonds), 0.9 (cyan triangles), 1.3 (blue squares), or 2.0 (red dots) mM ATP and 5 mM MgCl2/5 mM CaCl2/40 mM NaHCO3. Data represent individual points of a serial dilution of an experiment repeated three times. (d) Crystal structure of a sAC/ApCpp/LRE1 complex. The substrate analog ApCpp in the active site and the inhibitor in the BBS are shown as sticks colored according to atom type and overlaid with 2Fo-Fc electron density contoured at 1σ (blue). Ca2+ is shown as yellow sphere. (e) Overlay of sAC/ApCpp/LRE1 (green) with a sAC/ApCpp complex (blue, RMSD 0.31 Å2 for Cα atoms). Ligands and key interacting residues are shown as sticks, and Ca2+ as a yellow sphere.