Figure 2. Site of expression and biological role of the nemamides.
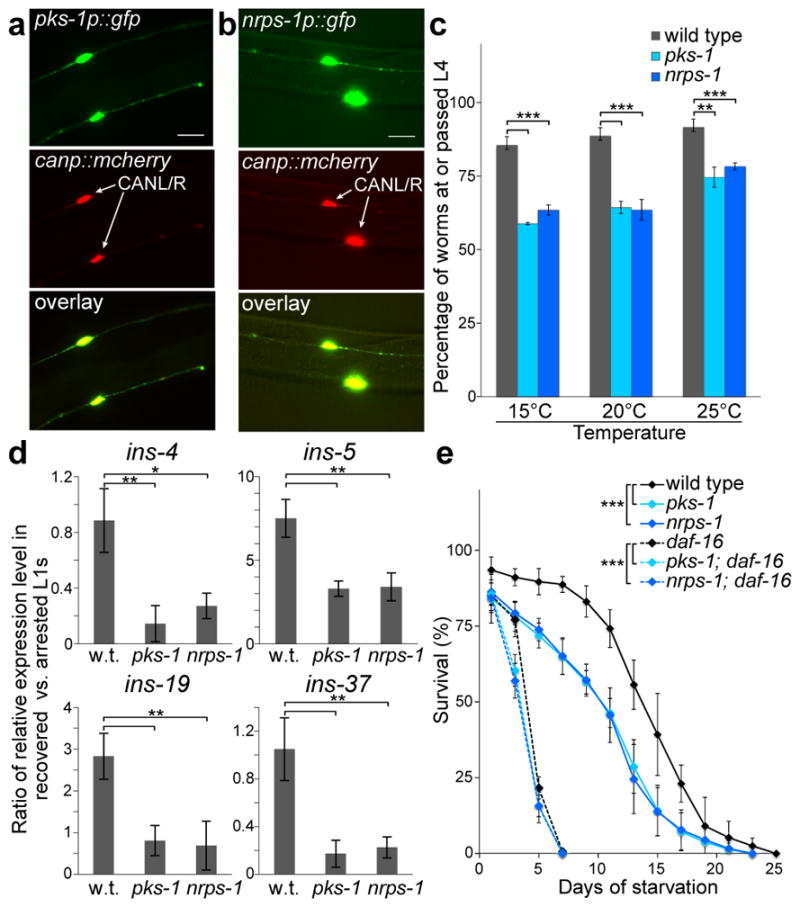
(a,b) Expression of the transcriptional reporters pks-1p::gfp (a) or nrps-1p::gfp (b), as well as canp::mcherry (marker for CAN neurons), in transgenic worms. Scale bar, 20 μm. We obtained similar results for pks-1p::gfp-pest and nrps-1p::gfp-pest reporters, in which GFP undergoes rapid turnover20. (c) Recovery of arrested L1s and development to the L4 stage for wild-type, pks-1, and nrps-1 worms at different temperatures. (d) Expression of specific insulins in recovered versus arrested wild-type, pks-1, and nrps-1 L1s, as determined by qRT-PCR. (e) Survival of wild-type, pks-1, and nrps-1 arrested L1s over time. The insulin/IGF-1 pathway controls L1 survival in a manner dependent on the downstream daf-16/foxo transcription factor15,21. The poor survival of daf-16/foxo (mu86 null) was slightly enhanced by the pks-1 and nrps-1 mutations. Mean survival (days ± SE): 14.3±0.2 for wild type, 11.3±0.3 for pks-1, 11.0±0.3 for nrps-1, 4.4±0.1 for daf-16, 3.7±0.1 for pks-1; daf-16, and 3.5±0.1 for nrps-1; daf-16. In c–e, the data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, and two-tailed, unpaired t-tests were applied (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001).
