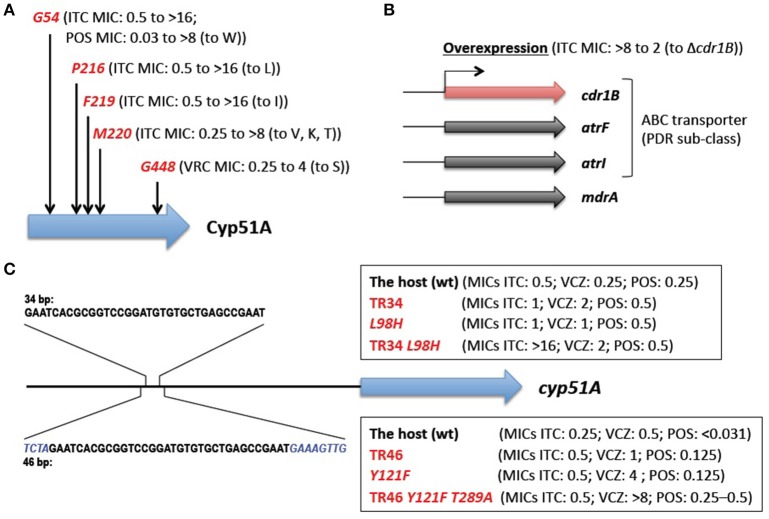
Figure 2.
Known azole resistance mechanisms in A. fumigatus. (A) Amino acid substitutions responsible for azole resistance. G54, P216, F219, M220, and G448 show the position at which amino acid changes resulted in azole resistance. The MICs of the strains harboring the change (to the indicated amino acid) are shown in parentheses (Mann et al., 2003; Mellado et al., 2004; Camps S. M. et al., 2012; Krishnan-Natesan et al., 2012). (B) The efflux transporters related to azole resistance. The MIC of the strain with overexpression of the cdr1B gene is shown in parentheses (Fraczek et al., 2013). (C) The tandem repeat sequences in a cyp51A promoter. The none-overlapping bases are shown in italics. The MICs of the strains harboring TR34 or TR46 and/or amino acid change(s) are shown in parentheses (Snelders et al., 2011, 2015). ITCZ, itraconazole; PSCZ, posaconazole; VRCZ, voriconazole.