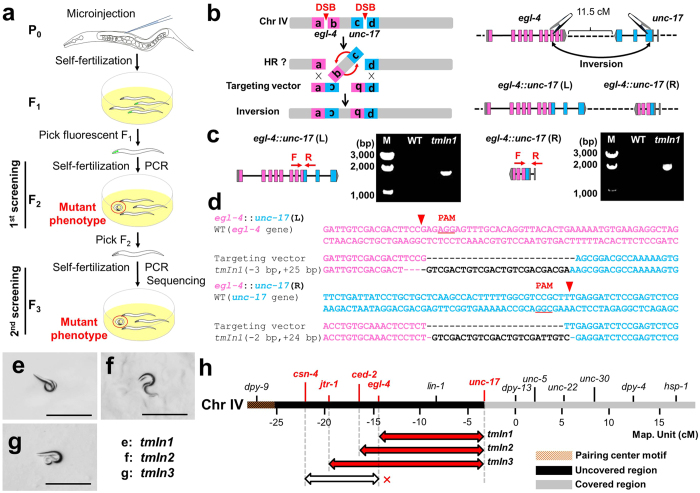
Figure 1. Genetic engineering of new balancers by using the CRISPR/Cas9 system.
(a) Experimental design to screen for inversion balancers. (b) Schematic of the chromosomal rearrangement tmIn1. tmIn1 was created by an inversion between egl-4 and unc-17. (c) PCR amplification of breakpoint junctions in wild-type (WT) and tmIn1 animals. (d) Breakpoint sequence alignments of the targeting vectors and tmIn1 rearrangement. Black bars indicate the cleavage sites. (e) The relative positions of breakpoints on chromosomal balancer IV. The generated balancers are indicated by red double-headed arrows. A white arrow with a cross indicates a failed trial. (f,g,h) Generated balancers showed a recessive larval arrest phenotype. Scale bars represent 100 μm.