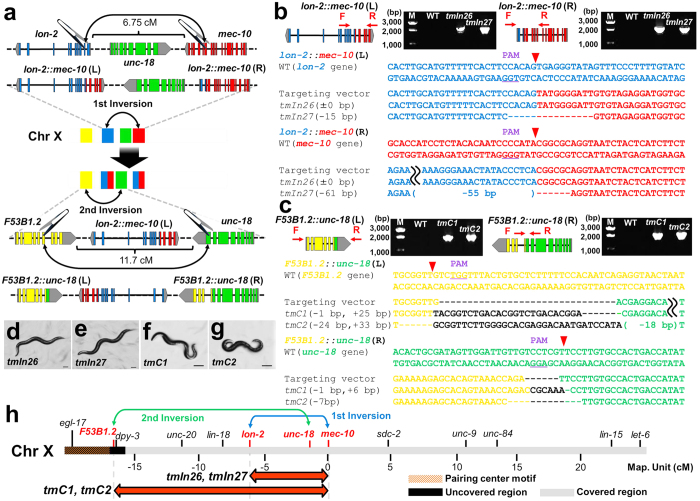
Figure 2. Genetic engineering of crossover-suppressors by using the CRISPR/Cas9 system.
(a) Schematic of a crossover-suppressor. The Crossover-suppressor was created by the multiple inversions. (b) PCR amplification of the breakpoint junctions in wild-type (WT), tmIn26 and tmIn27 animals. Breakpoint sequence alignments of the targeting vectors and tmIn26 and tmIn27 rearrangements. Black bars indicate the predicted cleavage sites. (c) PCR detection of the breakpoint junctions in WT, tmC1 and tmC2 animals. Breakpoint sequence alignments of targeting vectors and tmC1 and tmC2 rearrangements. (d) The relative positions of breakpoints in the X chromosomal balancers. (e,f) tmIn26 and tmIn27 showed a recessive long phenotype. (g,h) tmC1 and tmC2 showed a recessive uncoordinated phenotype. Scale bars represent 100 μm.