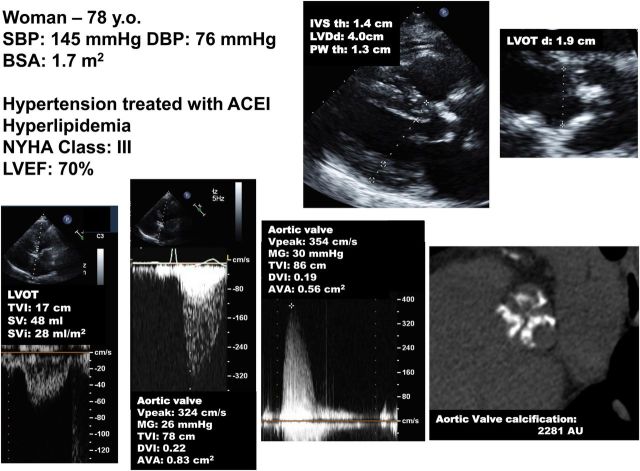
Figure 5.
Patient with paradoxical (preserved left ventricular ejection fraction) low-flow, low-gradient severe aortic stenosis. This case underlines the importance of multi-window continuous-wave Doppler interrogation for the measurement of the aortic velocity and gradient. In this patient, the gradient was higher at the right parasternal window than at the apical window. It is also important to rule-out error in the measurement of stroke volume. In this patient, the stroke volume measured by pulsed wave Doppler in the LVOT (48 mL) is corroborated by the stroke volume obtained with the modified Teichholz method: LV end-diastolic volume by Teichholz (70 mL) × left ventricular ejection fraction by biplane Simpson (70%) = 49 mL. The patient is in low flow (SVi: 28 mL/m2). Aortic valve calcium score by multi-detector computed tomography corroborates presence of true-severe stenosis. ACEI, angiotensin conversion enzyme inhibitor; BSA, body surface area; DVI, Doppler velocity index; LVDd, LV end-diastolic diameter; IVS th, interventricular septum thickness; PWth, posterior wall thickness; SBP/DBP, systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Other abbreviations as in Figures 1, 2, and 3.