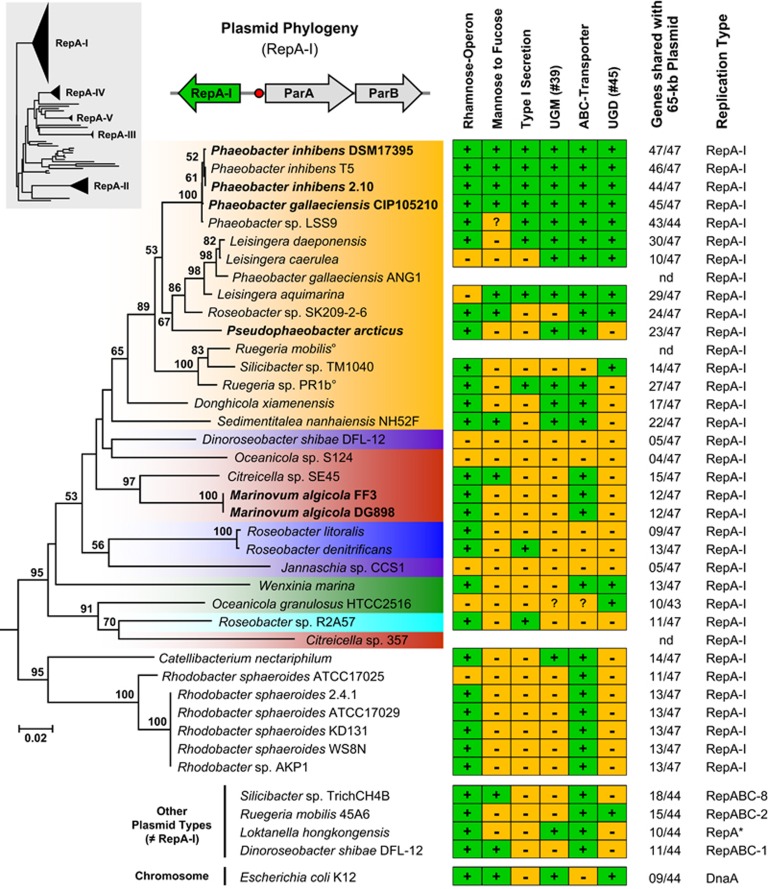
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree based on gamma-corrected distances of RepA-I-type plasmid replication initiator proteins from 35 Rhodobacteraceae sequences using 300 amino-acid positions. The color code corresponds to those of the phylogenomic tree (Figure 1). Strains of the current study whose RepA-I biofilm plasmid was cured are shown in bold. The topology of a comprehensive reference phylogeny containing all RepA-type proteins from the Roseobacter group is shown in the gray box (Supplementary Figure 3). The three genes represent a typical RepA-I-type plasmid replication module containing the replicase (repA-I), the parAB partitioning operon and the origin of replication (red circle). The matrix shows the presence and absence of central genes involved in polysaccharide metabolism using the biofilm plasmid of Phaeobacter inhibens DSM 17395 as a reference (Supplementary Table 1). UGM, UDP-galactopyranose mutase (EC 5.4.99.9); UGD, UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.22); °, genome not sequenced; *, compatibility group not determined.