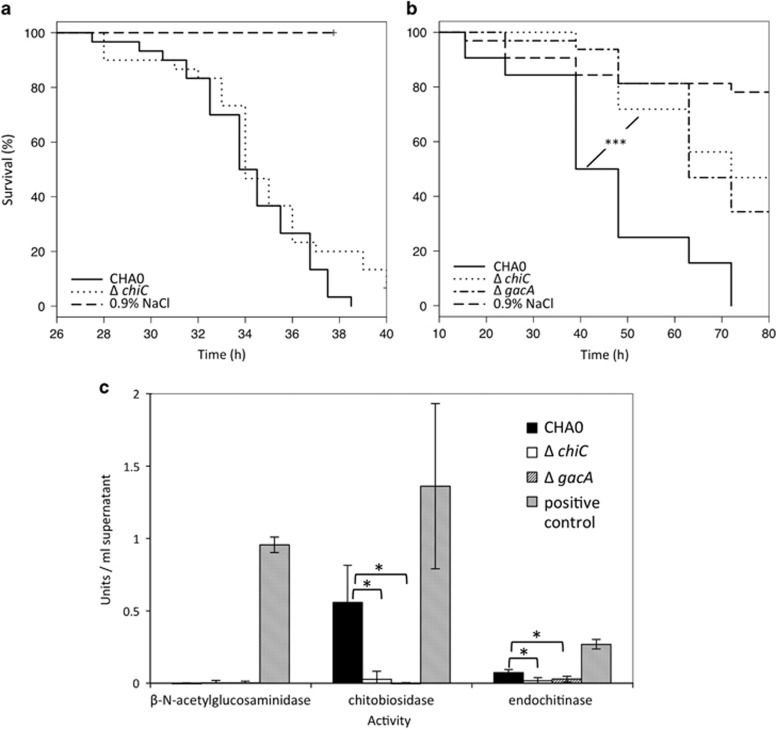
Figure 4.
A derivative of P. protegens CHA0 deficient for a specific chitinase is reduced in oral, but not in injectable activity against insect larvae. (a) Systemic activity against G. mellonella. Thirty larvae per treatment were injected with 2 × 103 bacterial cells and survival was recorded hourly. (b) Oral activity against P. xylostella. Larvae were exposed to artificial diet inoculated with 4 × 106 bacterial cells. Significant differences according to a Log-Rank test (Survival Package in R) between treatments with the wild-type CHA0 and the chitinase C-negative mutant (ΔchiC) are indicated with ***P<0.0001. Each mutant was tested at least three times with similar results. A repetition of the feeding assay is depicted in Supplementary Figure S5. (c) Chitinase activity of wild-type CHA0 and its chiC mutant was assessed using a chitinase assay kit (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA). Three different substrates were used to test for exo- (β-N-acetylglucosaminidase and chitobiosidase) and endochitinase activity. Treatments indicated by an asterisk are significantly different based on a t-test (P⩽0.05). CHA0, wild type; ΔchiC, chitinase C-negative mutant; ΔgacA, GacA-negative mutant; 0.9% NaCl served as negative control in the virulence assay; a positive control for chitinase activity was provided by the chitinase assay kit.