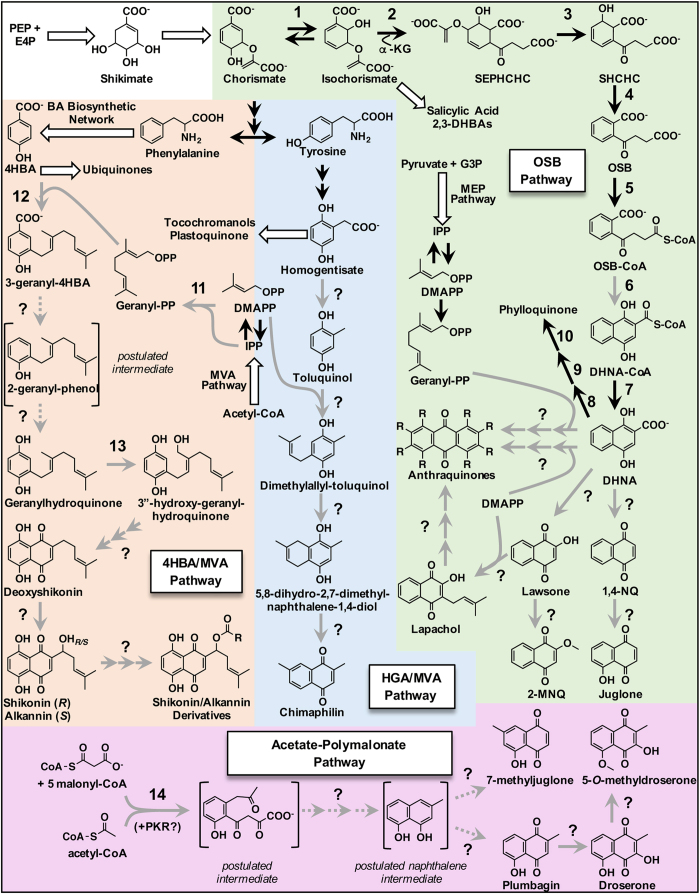
Figure 2.
The plant 1,4-NQ biosynthetic network. Presented is the current understanding of the enzymes and intermediates involved in the core metabolic pathways for synthesizing 1,4-naphthalenoid rings in plants and for producing some of the major horticultural 1,4-NQs. Subcellular architecture is not depicted but is discussed in the text. Black arrows indicate the existence of genetic evidence to support biosynthetic reactions, while gray arrows signify a lack of genetic evidence. Tandem triplicate arrows indicate an unknown number of multiple steps to go from a given intermediate to the next metabolite. Dotted arrows are used to represent steps to and from postulated intermediates. White block arrows represent entire metabolic pathways to relevant or noteworthy metabolites not addressed in this review. Question marks next to arrows indicate that enzymatic activities for those steps have not been described. Numbers next to arrows represent characterized enzymes or detected enzymatic activities: 1, isochorismate synthase; 2, 2-succinyl-5-enolpyruvyl-6-hydroxy-3-cyclohexene-2-carboxylate (SEPHCHC) synthase; 3, 2-succinyl-6-hydroxy-2,4-cyclohexadiene-2-carboxylate (SHCHC) synthase; 4, o-succinylbenzoate (OSB) synthase; 5, OSB-CoA ligase; 6, Dihydroxynaphthoyl-CoA (DHNA-CoA) synthase; 7, DHNA-CoA thioesterase; 8, Dihydroxynaphthoic acid (DHNA) phytyl transferase; 9, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase C1 (NDC1); 10, Demethylphylloquinone methyltransferase; 11, cytosolic geranyl diphosphate synthase (GPPS); 12, p-hydroxybenzoate:geranyltransferase (PGT); 13, geranylhydroquinone (GHQ) 3″-hydroxylase; 14, polyketide synthase (PKS). BA, benzoic acid; DHBA, dihydroxybenzoic acid; DMAPP; dimethylallyl diphosphate; E4P, D-erythrose 4-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; MEP, methylerythritol 4-phosphate; MVA, mevalonic acid; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PKR, polyketide reductase; PP, diphosphate.