FIGURE 1.
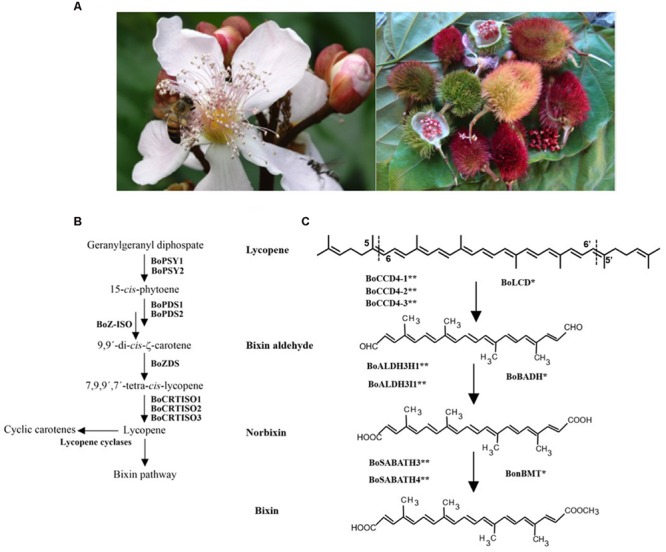
(A) Bixa orellana L. buds, flower (left), fruit and seeds (right). (B) Carotenoid biosynthesis Pathway. Carotene biosynthesis start with the phytoene synthesis by condensation of two geranilygeranyl diphosphate molecules mediated by phytoene synthase enzymes (BoPSY1 and BoPSY2). The phytoene is convert to Lycopene by successive steps of desaturation (phytoene desaturase: BoPDS1 and BoPDS2; ζ-carotene desaturase: BoZDS) and isomerization (ζ-carotene isomerase: BoZ-ISO; Carotenoid isomerase: BoCRTISO1, BoCRTISO2 and BoCRTISO3). (C) Bixin biosynthesis pathway. Lycopene is convert into bixin by three serial step reactions. (1) Lycopene is cleaved at the 5-6 and 5′-6′ double bonds by carotenoid cleavage enzymes from family 4 (BoLCD; BoCCD4-1: KT359022; BoCCD4-2: KT359023; BoCCD4-3: KT359024). (2) Bixin aldehyde is the oxidation product of aldehyde groups by aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes (BoBADH; BoALDH3I1: KT359036; BoALDH3H1: KT359033). (3) Norbixin is converted into bixin by the addition a methyl group in carboxyl groups by a methyl transferase enzyme belonging to SABATH methyl transferase family (BonBMT; BoSABATH3: KT359051; BoSABATH4: KT359052). Dashed lines indicate the position of lycopene cleavage. A single asterisk indicates the proved enzymes that convert lycopene into bixin. A double asterisk indicates the proposed new set of genes involved in bixin synthesis.
