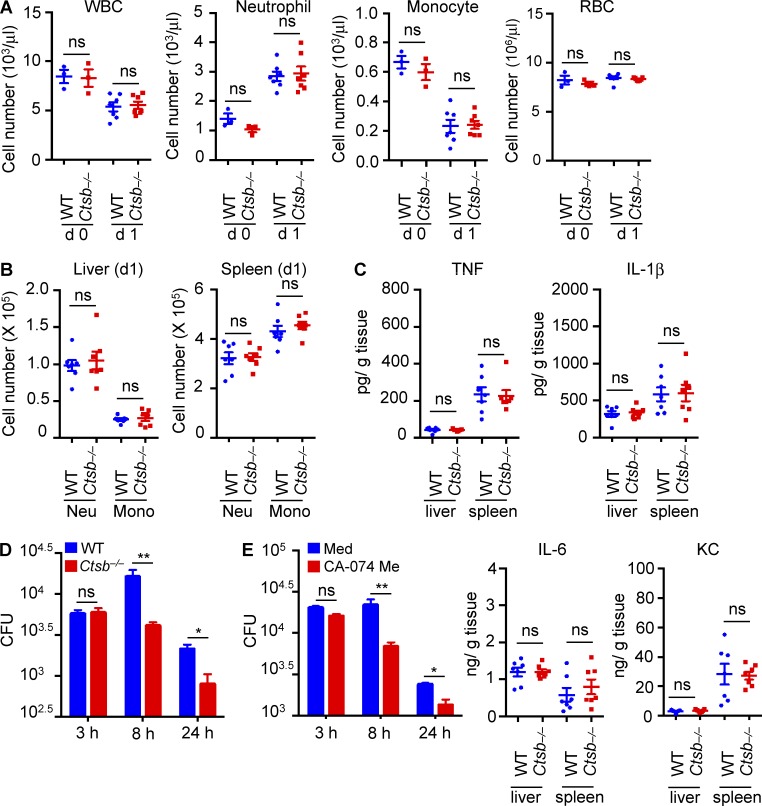
Figure 2.
Macrophages lacking cathepsin B have enhanced bactericidal activity. (A) Blood cells from uninfected mice (d 0) or mice infected with F. novicida (d 1) were analyzed for different cell populations with a Forcyte hematology analyzer. WBC, white blood cell. (B) On day 1 after F. novicida infection, neutrophil (CD11b+ Ly6g+; Neu) and monocyte (CD11b+ Ly6g−; Mono) infiltration into the liver and spleen were analyzed. (C) Cytokine levels were measured in the liver and spleen from WT and Ctsb−/− mice on day 1 after infection with F. novicida. (D) BMDMs from WT and Ctsb−/− mice were infected with F. novicida (MOI 10) for 3 h, and numbers of intracellular bacteria were enumerated at the indicated times. (E) BMDMs from WT mice were infected with F. novicida (MOI 10) for 3 h in media (Med) with or without the cathepsin B inhibitor CA-074 Me (5 µM). The number of intracellular bacteria was enumerated at the indicated times. KC, keratinocyte-derived chemokine. Each symbol indicates an individual mouse and means ± SEM are shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments for A–C or three independent experiments for D and E. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. ns, not significant.