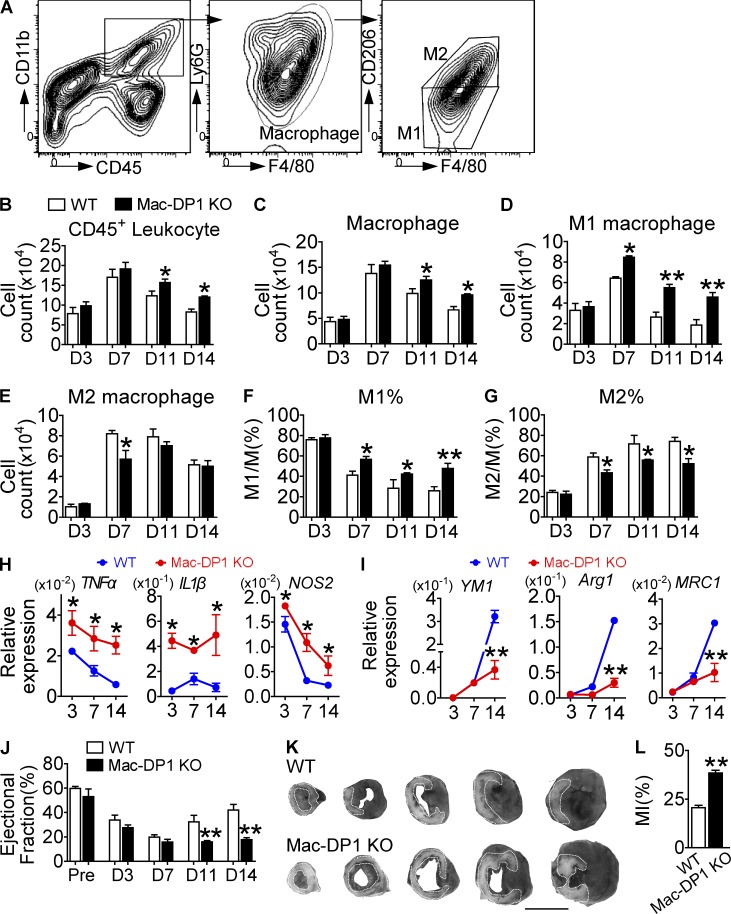
Figure 4.
DP1 deletion in macrophages impairs MI healing by suppressing M2 polarization and resolution in ischemic hearts. (A–G) Effect of DP1 deficiency in macrophages on inflammatory resolution during post-MI recovery. (A) Inflammatory cell infiltrate in infarcted hearts was isolated from both WT and Mac-DP1 KO mice. (B–G) Total CD45+ leukocytes (B), CD45+CD11b+ F4/80+Ly6G− macrophages (C), and F4/80+CD206− and F4/80+ CD206+ cells (D and E) and their ratios (F and G) were calculated at different time points. n = 4–6. (H and I) Effect of DP1 deletion on mRNA expression of proinflammatory genes (H) and antiinflammatory genes (I) in macrophages infiltrated in hearts. n = 6. (J and K) Effect of DP1 deficiency in macrophages on post-MI recovery in mice. (J) The ejection fraction was evaluated by echocardiography. Pre, pre-ligation. n = 10–14 per group. (K) Infarct areas were analyzed at day 14 by Evans blue dye and tetrazolium chloride staining, followed by OPTIMAS software analysis for color enhancement. Dotted lines denote the infarct zone. The darkest area is normal heart tissue, whereas the gray area represents at-risk myocardial tissue. Bar,10 mm. (L) Quantitation of infarcted areas. n = 6. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 versus WT. Representative data are shown as mean ± SEM derived from two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student's t tests.